Data Sync Select Objects
Learn how to select and filter synchronization objects in Data Sync. This comprehensive guide covers basic filtering, regular expressions, and best practices for object selection.
By default, Data Sync synchronizes all tables in the selected database. Object filtering allows you to customize which objects are synchronized, providing granular control over:
- Database Selection: Include or exclude specific databases
- Schema Filtering: Include or exclude specific schemas
- Table Selection: Include or exclude specific tables
You can select objects using two methods: basic filtering for simple selections, or regular expression filtering for complex pattern-based selections.
Basic Filtering
This section demonstrates object selection using MySQL as an example.
Database Selection
Default State: All databases are selected by default.
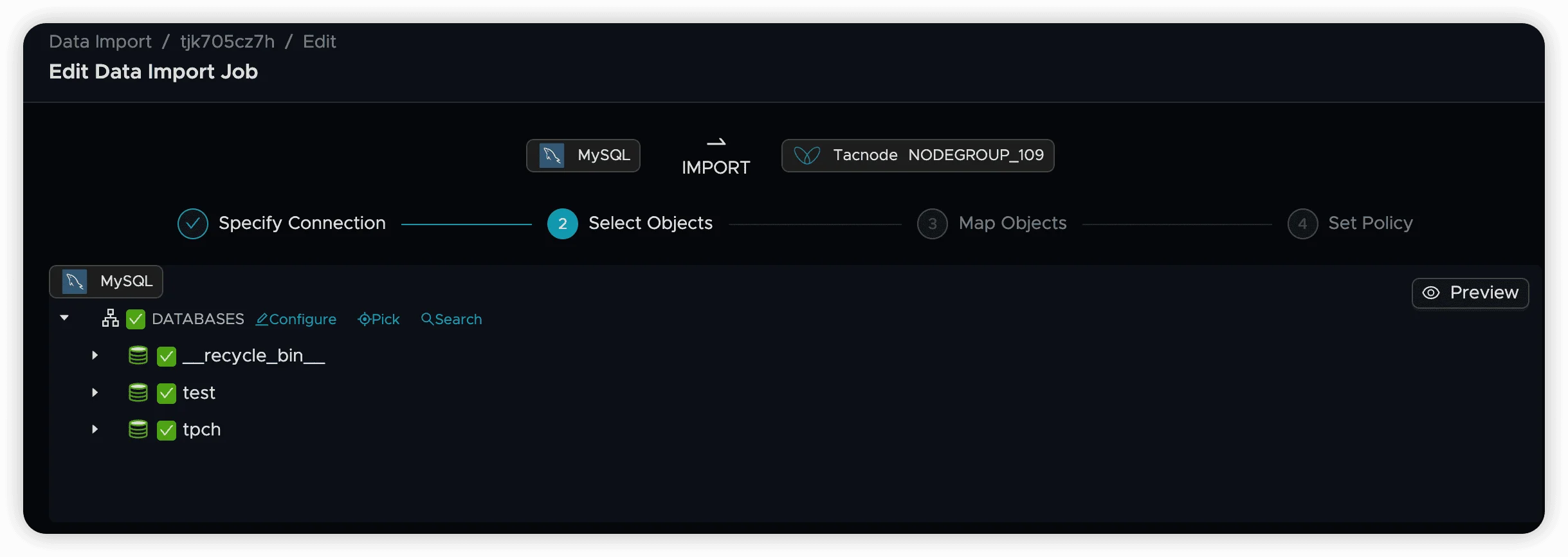
Include/Exclude Databases: Check or uncheck databases to include or exclude them from synchronization. When a database is unchecked, its tables become unavailable and cannot be synchronized.
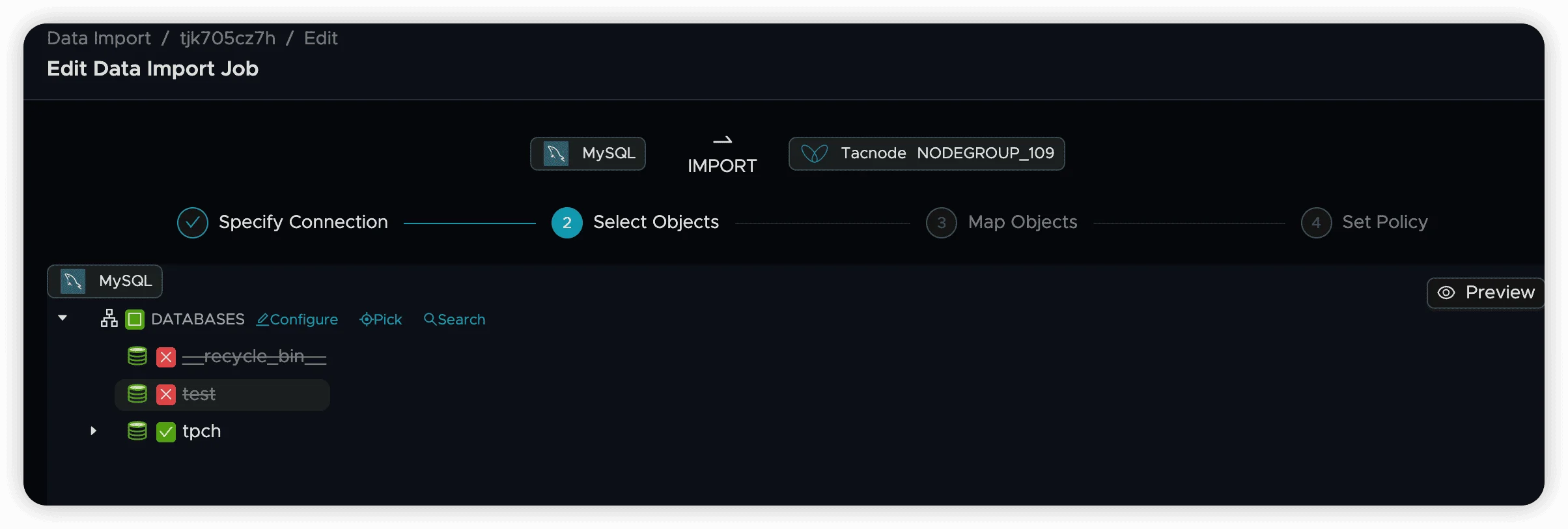
Search Databases: Use the search functionality to quickly find databases by name.
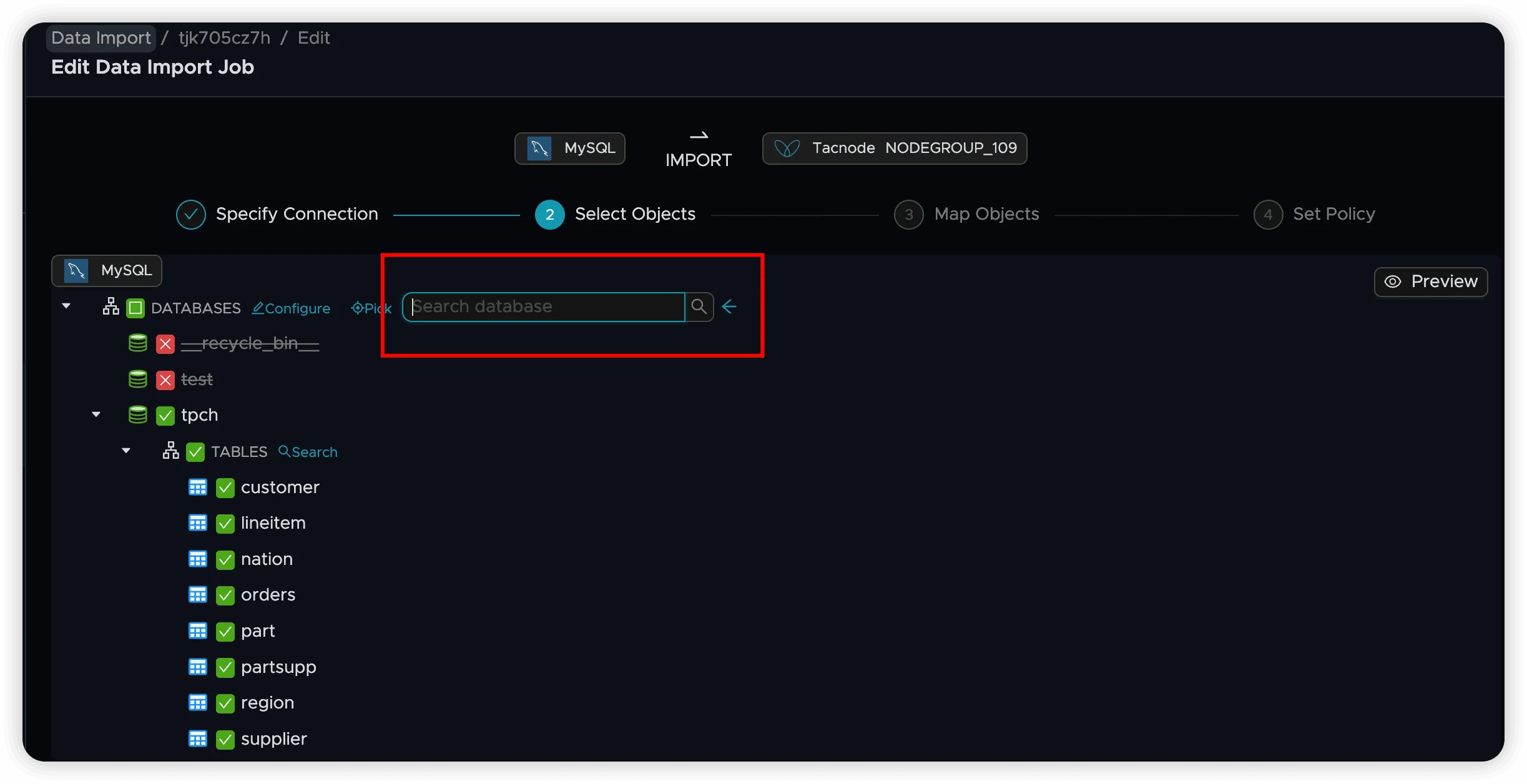
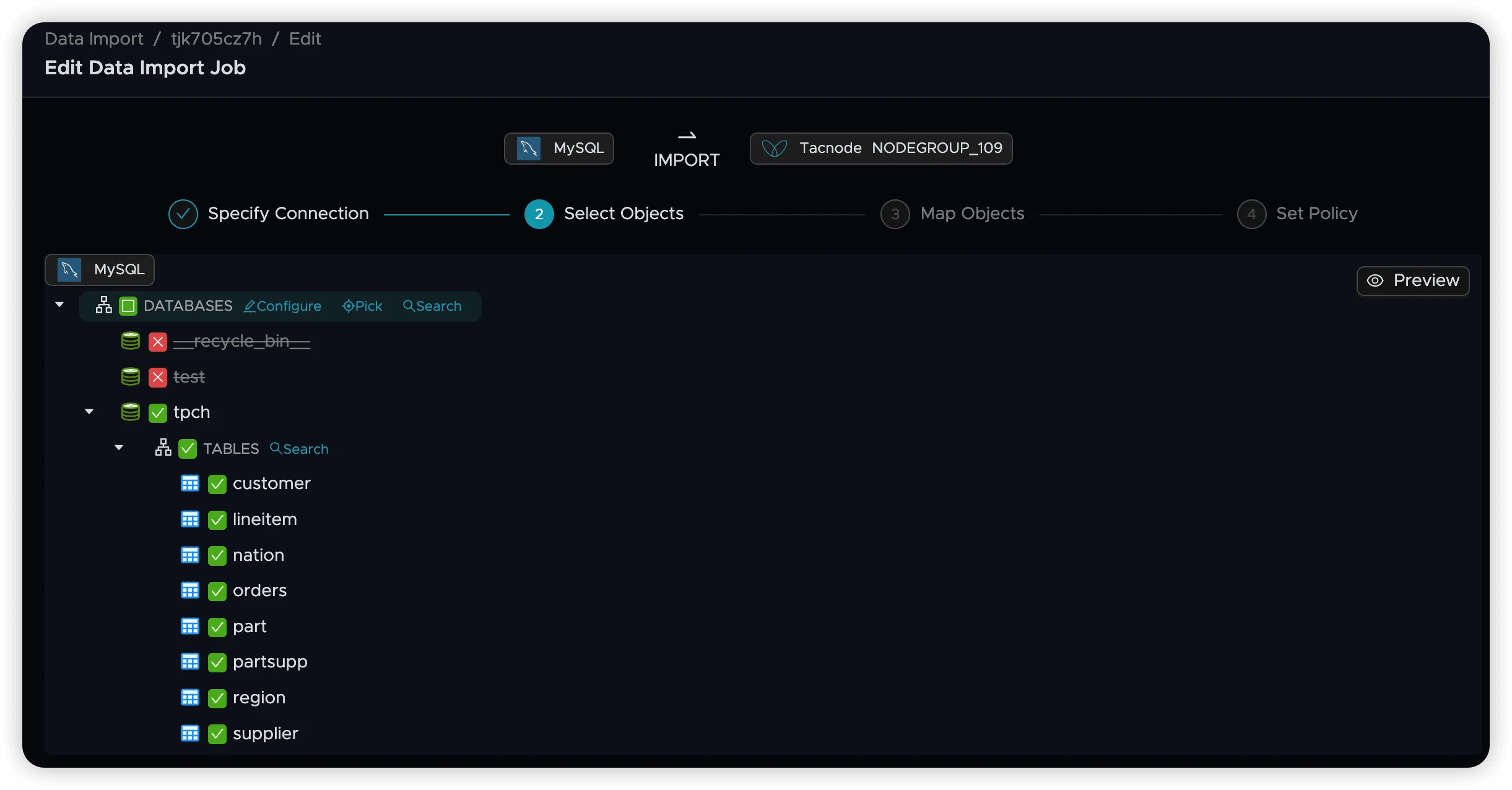
Table Selection
Table Organization: In MySQL, tables are organized under databases. Expand a database to view its tables.
Default State: When a database is expanded, all its tables are selected by default.
Include/Exclude Tables:
- Check or uncheck individual tables to control synchronization
- Use the TABLES node controls to select all or deselect all tables within a database
Regular Expression Filtering
For large numbers of objects, use regular expressions to filter based on naming patterns (prefixes, suffixes, etc.).
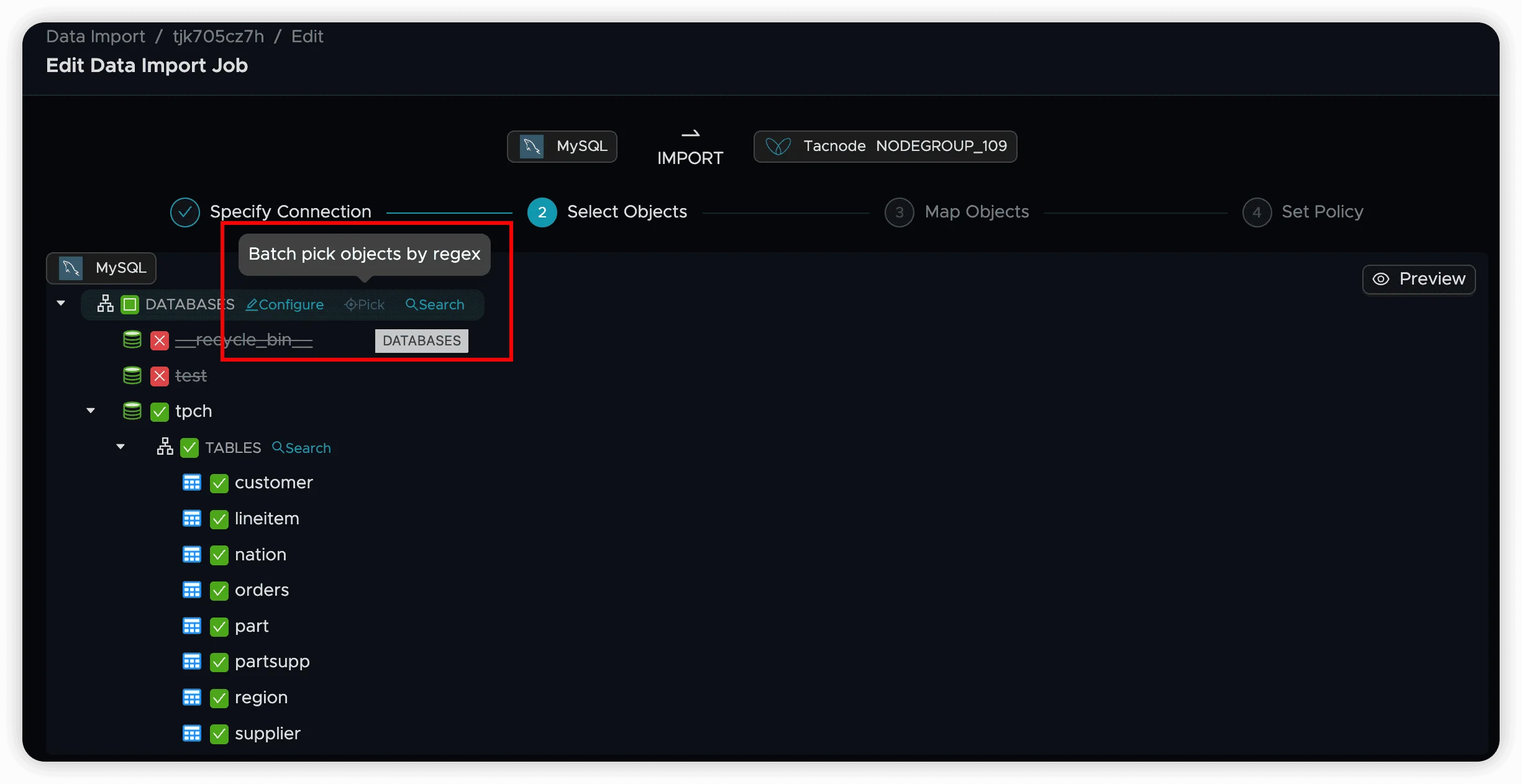
Regular expression filtering offers two editing modes: Form Mode and Editor Mode.
Form Mode
Form Mode provides a user-friendly interface for creating filtering rules:
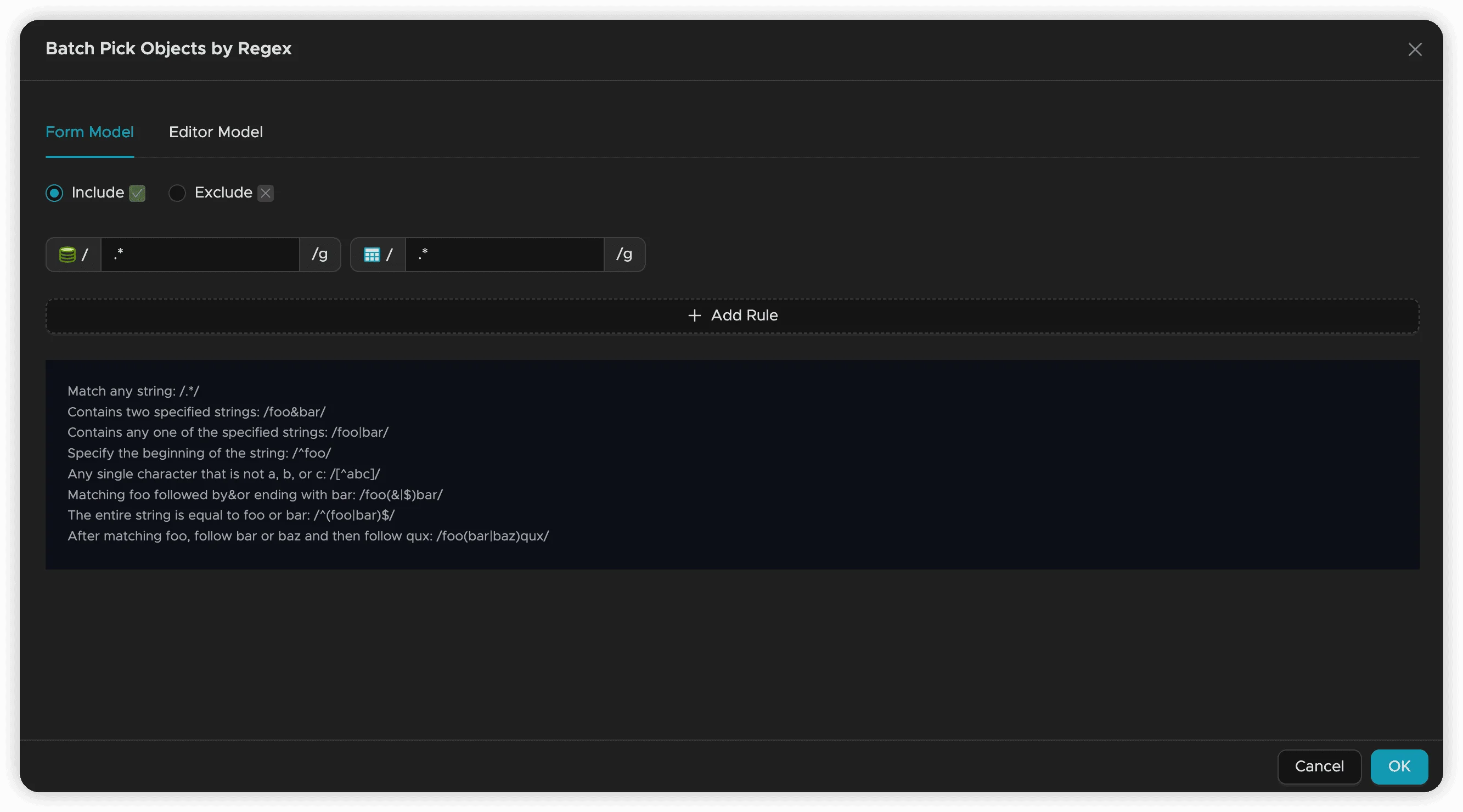
Configuration Steps:
- Action: Choose whether to include or exclude objects matching the pattern
- Database Pattern: Enter a regular expression for database names (leave blank to match all)
- Table Pattern: Enter a regular expression for table names (leave blank to match all)
- Rule Relationships:
- Database and Table patterns are combined with AND logic
- Multiple rules are combined with OR logic
- Add Rules: Click Add Rule to create additional filtering criteria
Example: To synchronize only tables starting with “user_” in databases ending with “_prod”:
- Database Pattern:
.*_prod$ - Table Pattern:
^user_.*
Editor Mode
Editor Mode allows direct JSON editing, useful for managing complex rule sets:
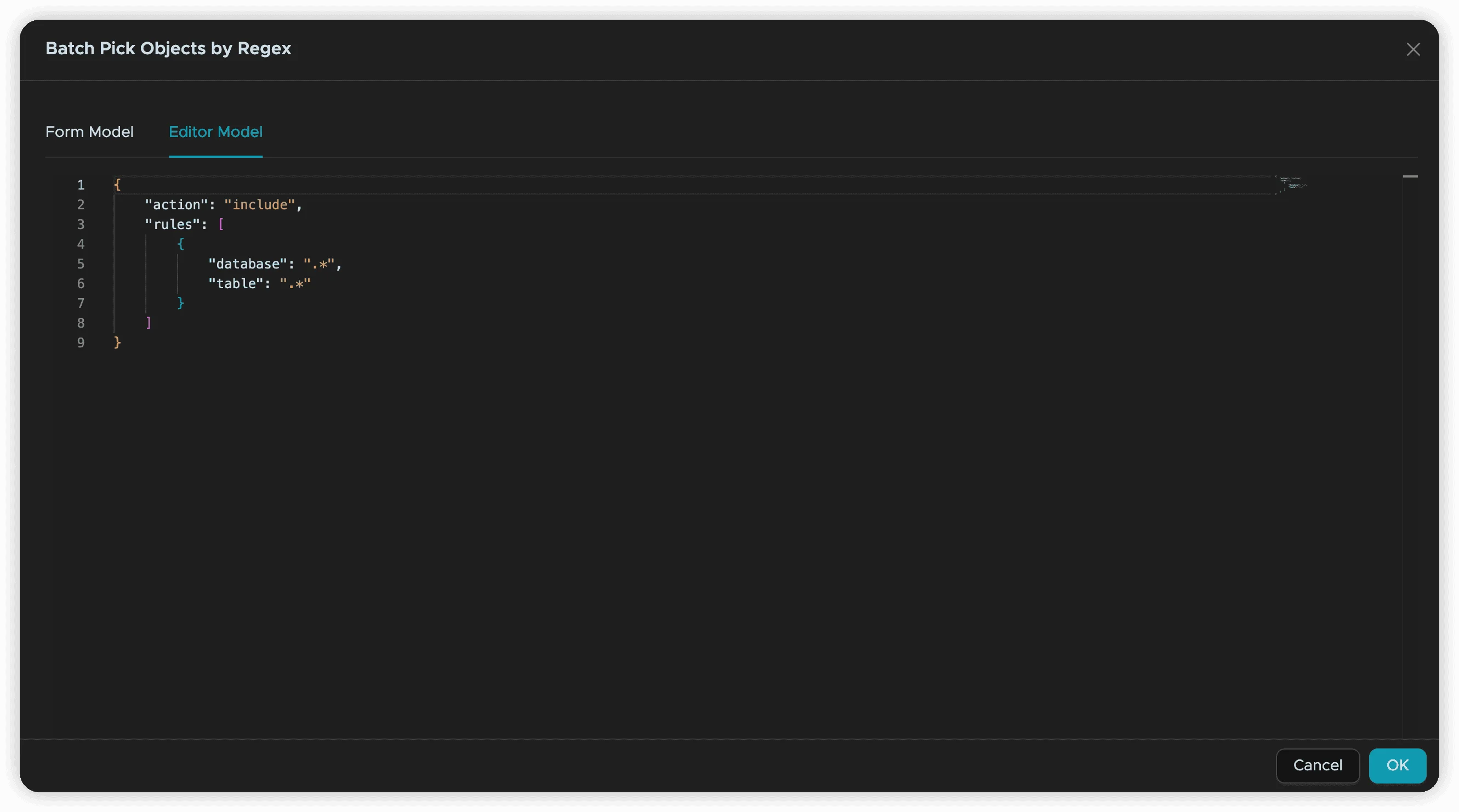
Key Features:
- Seamless Conversion: Rules created in Form Mode appear as JSON in Editor Mode
- Bidirectional Editing: Switch between modes while preserving rules
- Bulk Management: Ideal for handling many rules (e.g., 100+ table names)
JSON Format Example:
{
"rules": [
{
"action": "include",
"database_pattern": ".*_prod$",
"table_pattern": "^user_.*"
}
]
}Important Considerations
Synchronization Behavior
- Full Synchronization: If a database is selected but all its tables are excluded, no data will be synchronized initially
- Incremental Synchronization: If database-level CREATE permissions are enabled, newly created tables will be automatically synchronized even if the parent database had no initially selected tables
Configuration Dependencies
When configuring object selection, consider the synchronization policy settings:
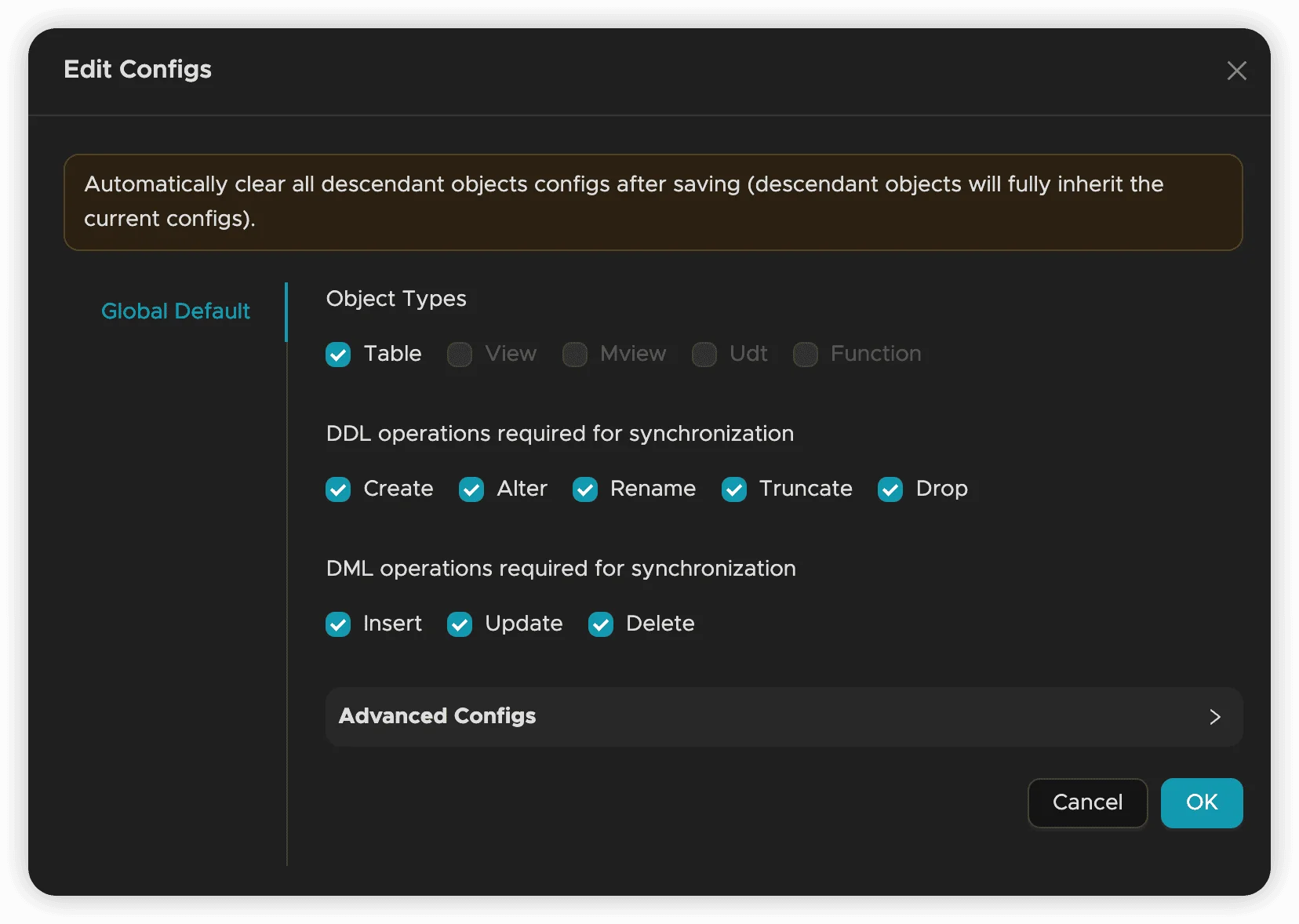
Best Practices:
- Start Broad, Then Narrow: Begin with default selections and exclude unwanted objects
- Test Patterns: Verify regular expressions match expected objects before starting synchronization
- Document Rules: Keep track of complex filtering logic for future reference
- Consider Growth: Design patterns that accommodate new objects as your data grows