Data Sync Map Objects
Learn how to configure object mapping in Data Sync. This comprehensive guide covers mapping rules, syntax, and practical examples for effective data transformation.
Object mapping defines how source objects (databases, schemas, tables) correspond to target objects in Tacnode. Each synchronization job has default mapping rules that can be customized to meet specific requirements.
Understanding Object Structure
Target objects in Tacnode follow the structure: database.schema.table
database: The database nameschema: The schema within the databasetable: The table name
Object mapping shows how each source object maps to its corresponding target object during synchronization.
Managing Mapping Rules
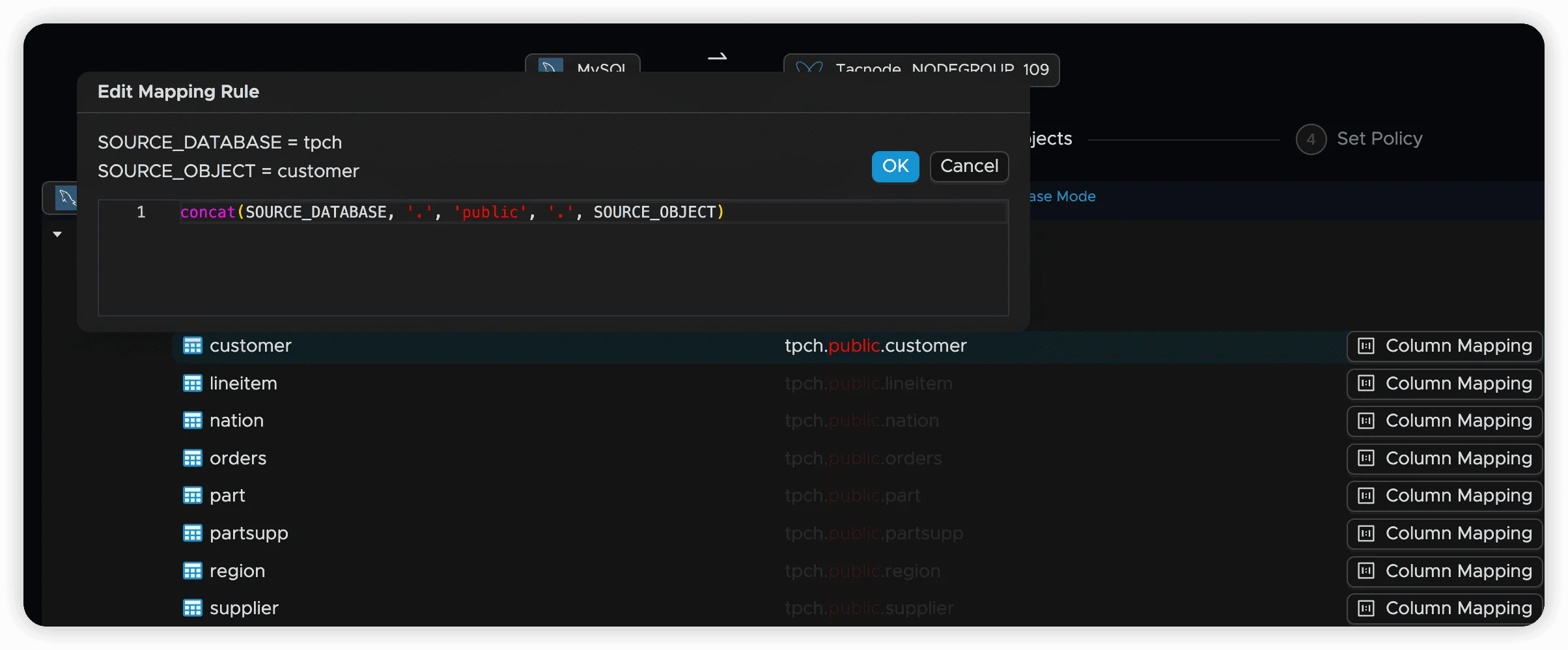
Edit Individual Mappings
Configure mapping rules for specific nodes, including changing node attributes and setting inheritance behavior.
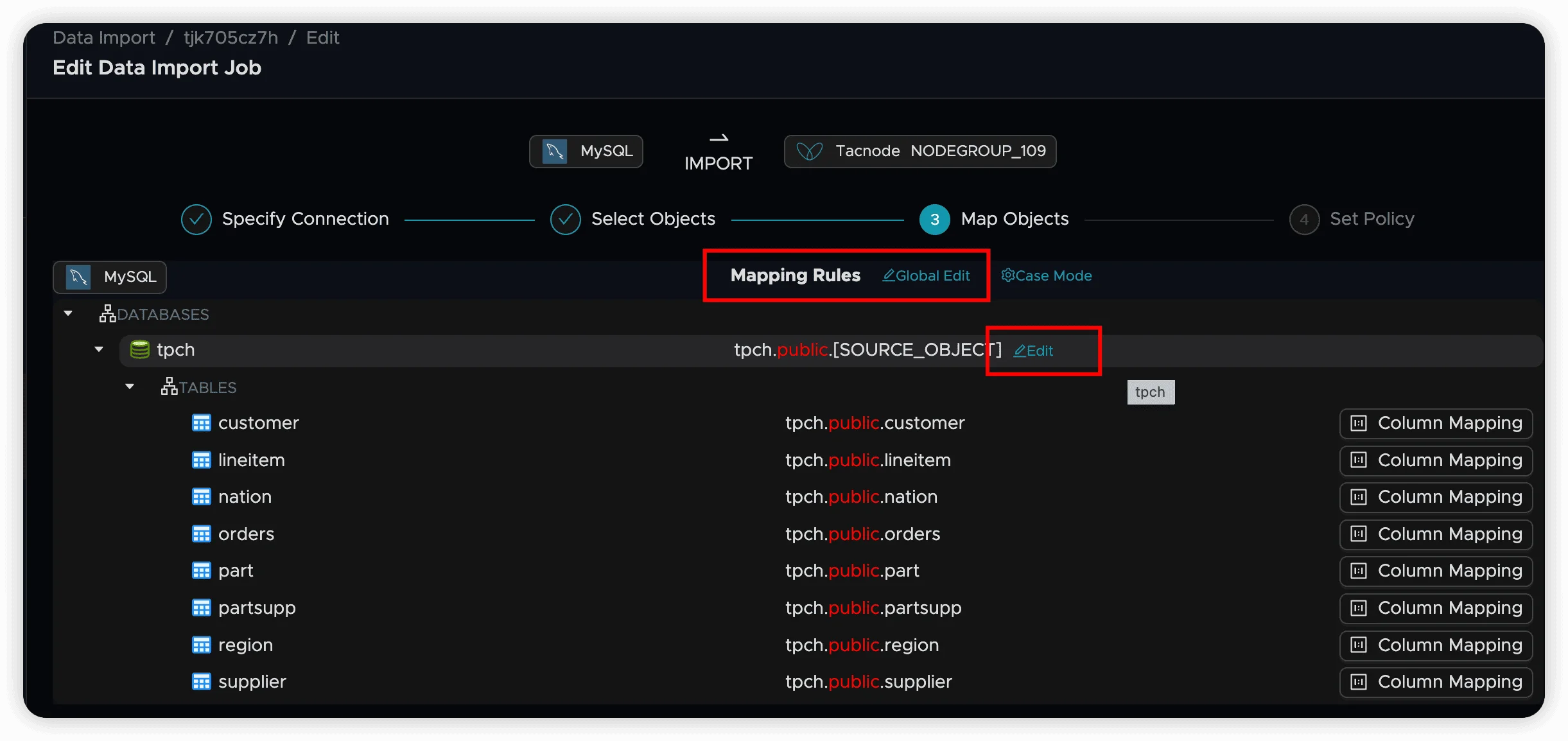
Global Edit Operations
Use the Global Edit button to apply mapping rules to multiple sibling nodes simultaneously, streamlining bulk configuration.
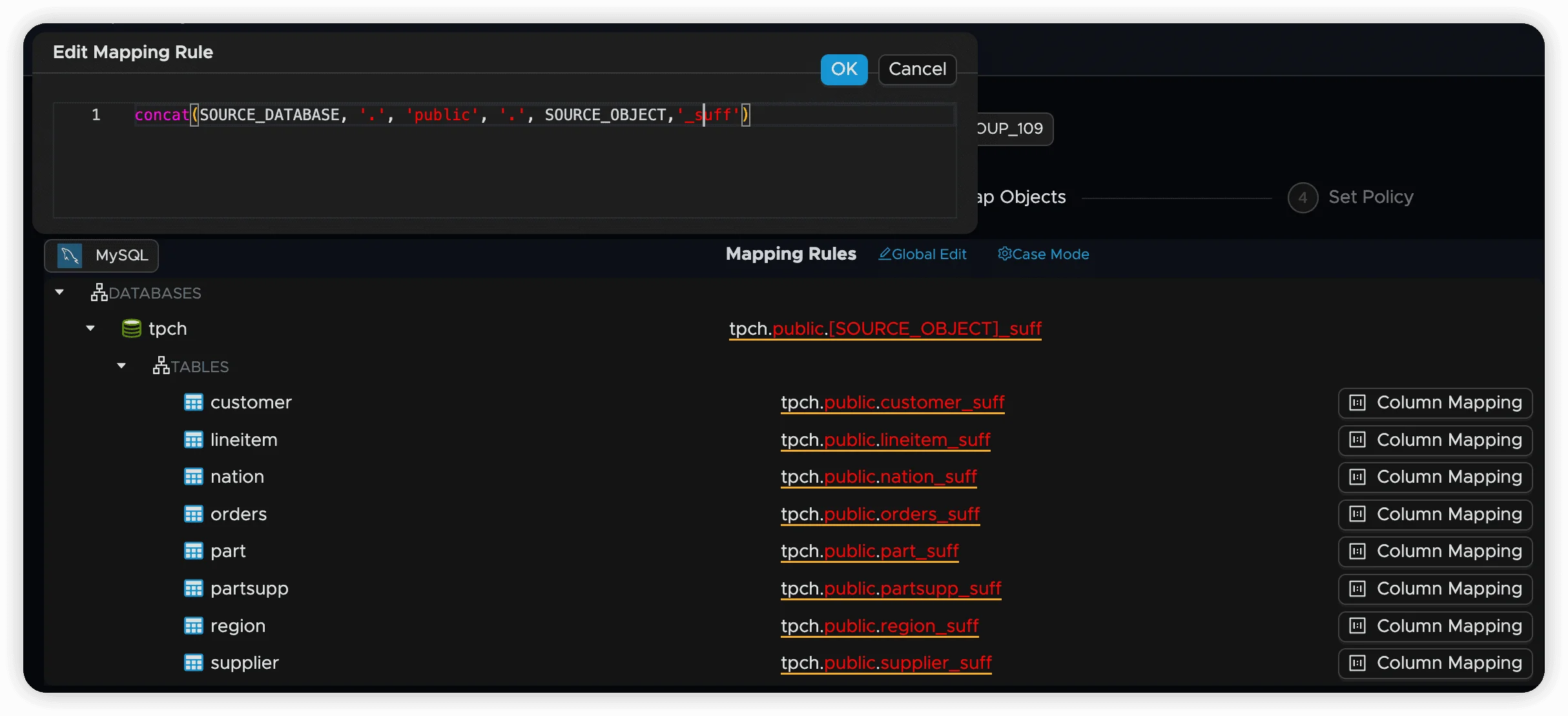
Mapping Rule Syntax
Data Sync supports three types of expressions for defining mapping rules:
1. Constants
Use single quotes to define static values:
'target_database.public.new_table'2. Concat Function
Combine constants and source variables using the concat function:
Available Source Variables:
SOURCE_DATABASE: Name of the source databaseSOURCE_SCHEMA: Name of the source schemaSOURCE_OBJECT: Name of the source object (table, view, function)
Example:
concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.', 'public', '.', SOURCE_OBJECT)This maps a source table to the same table name in the public schema of the target database.
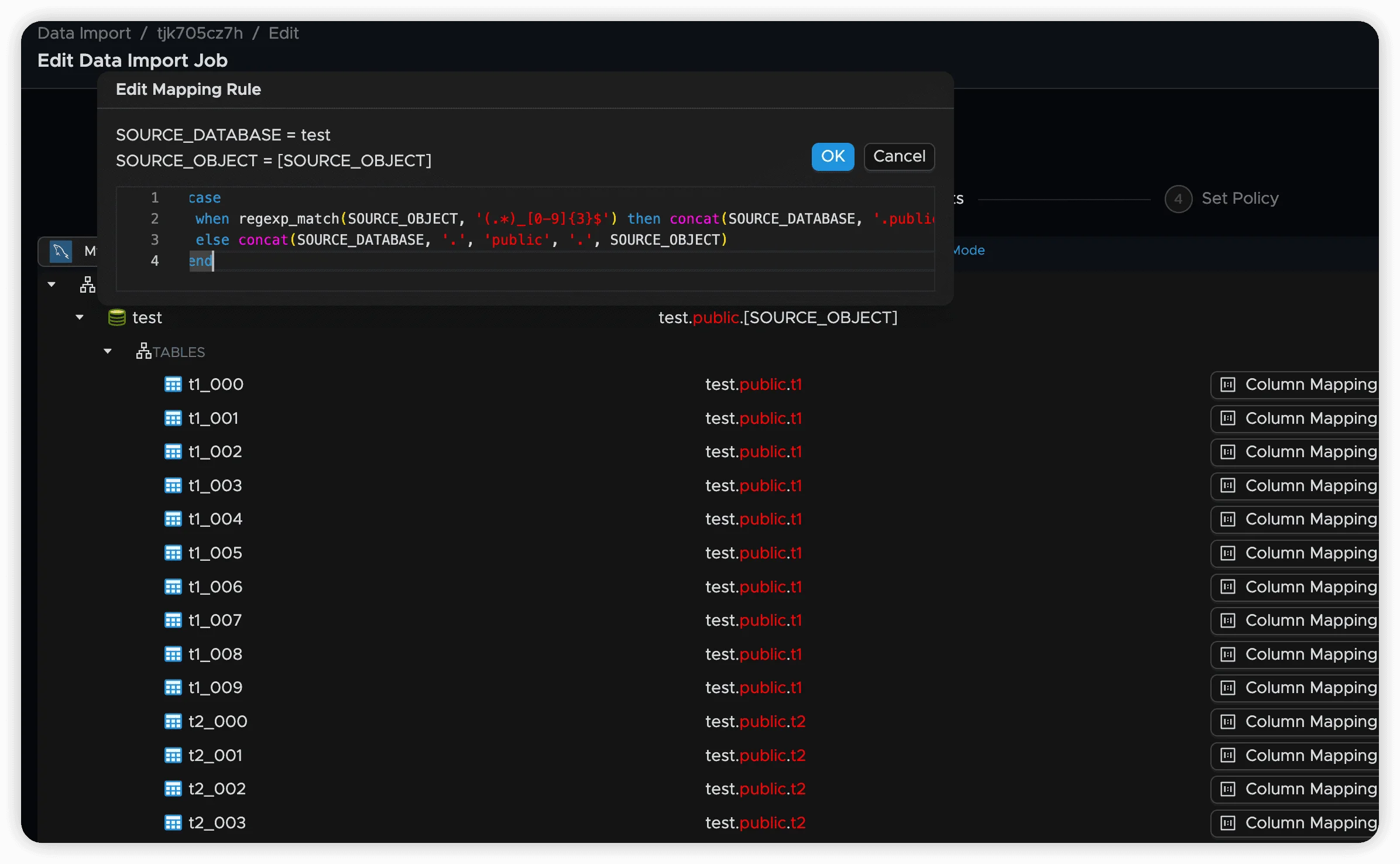
3. Case When Expressions
For complex mappings like consolidating sharded tables, use conditional logic:
case
when ${condition} then ${expression}
when ${condition} then ${expression}
else ${expression}
endSupported Conditions:
LIKE Pattern Matching:
case
when SOURCE_OBJECT like 'user_%' then concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.users')
when SOURCE_OBJECT like 'order_%' then concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.orders')
else concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.', SOURCE_OBJECT)
endRegular Expression Matching:
case
when regexp_match(SOURCE_OBJECT, '(.*)_[0-9]{3}$') then concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.', $1)
else concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.', SOURCE_OBJECT)
endIn regex patterns, captured groups are accessible as $1, $2, etc.
Practical Examples: MySQL to Tacnode
Example 1: Change Default Database and Schema
Map all tables to a different database and schema:
concat('target_database', '.', 'custom_schema', '.', SOURCE_OBJECT)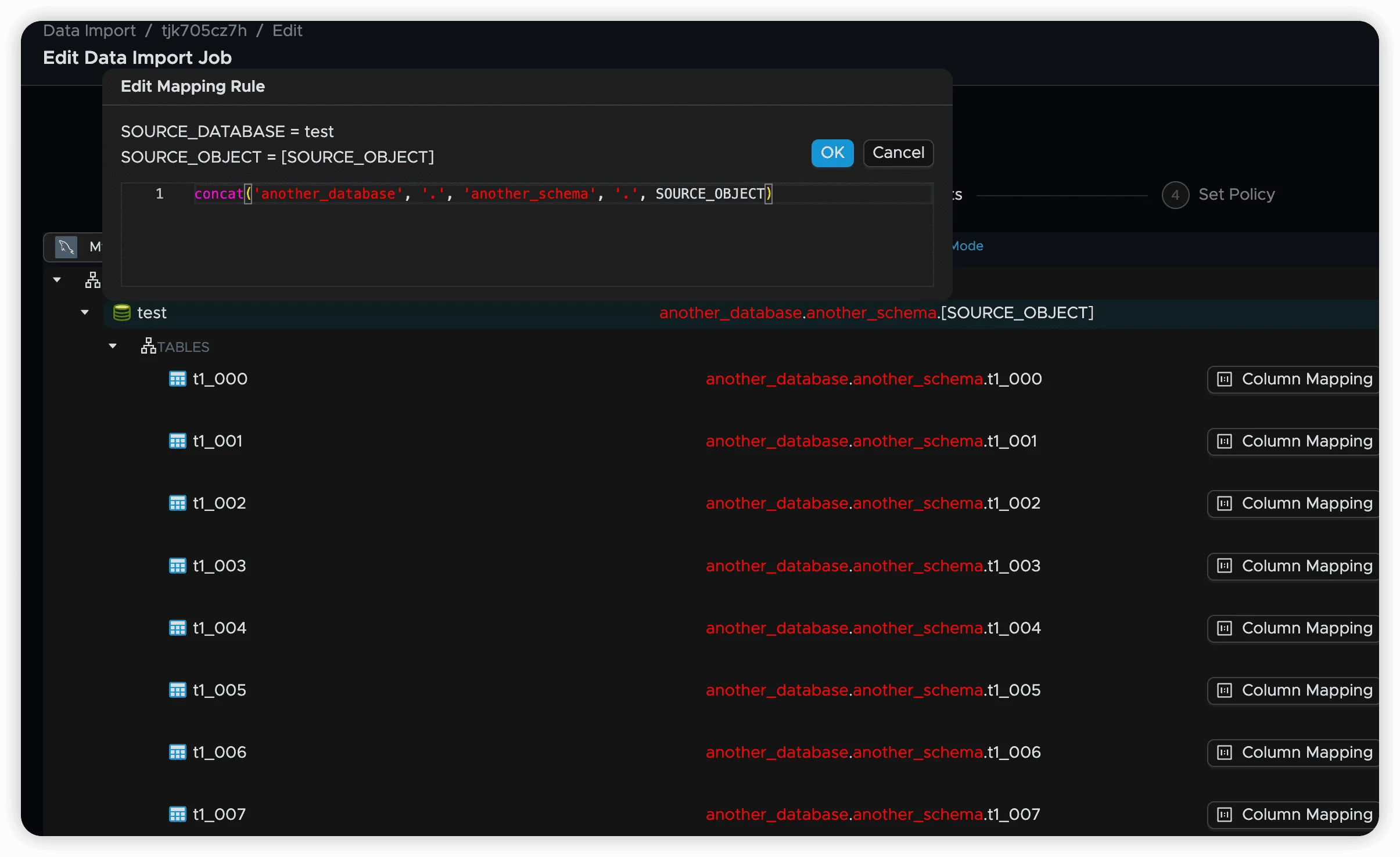
Example 2: Rename Specific Table
Change a specific table name during mapping:
concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.', 'public', '.', 'renamed_table')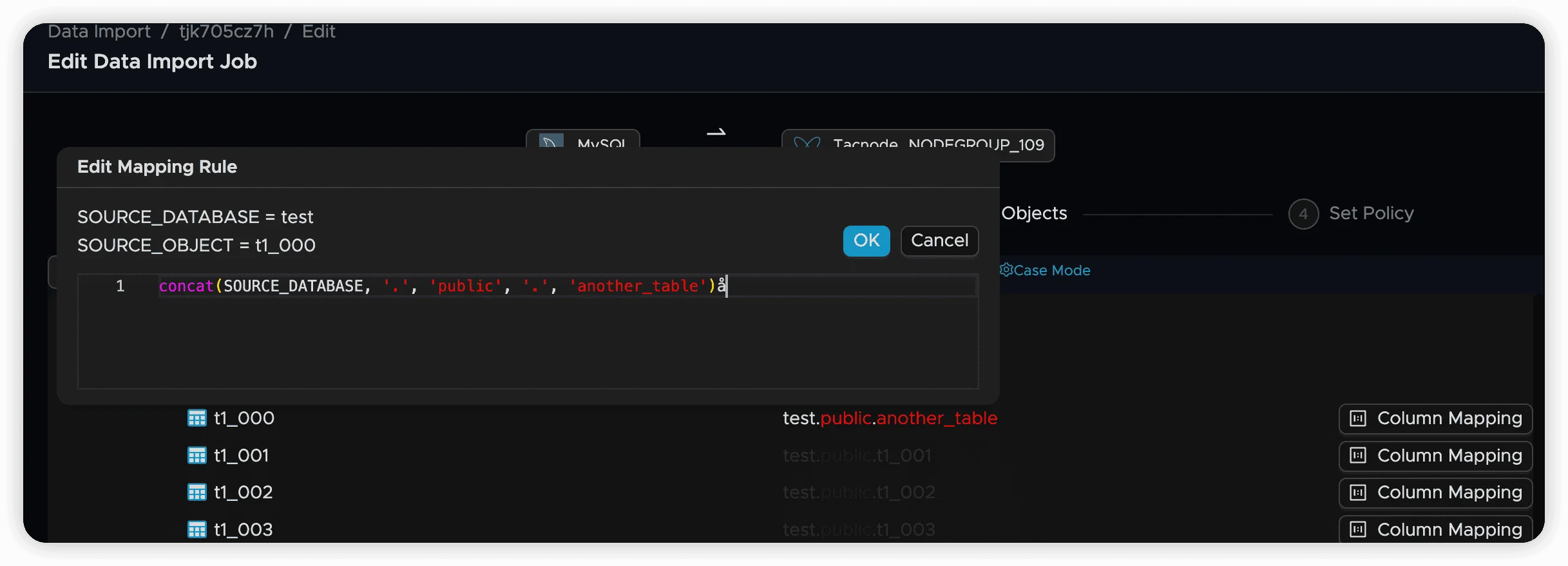
Example 3: Consolidate Sharded Tables
Using LIKE patterns:
case
when SOURCE_OBJECT like 'users_%' then concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.users')
when SOURCE_OBJECT like 'orders_%' then concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.orders')
else concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.', SOURCE_OBJECT)
end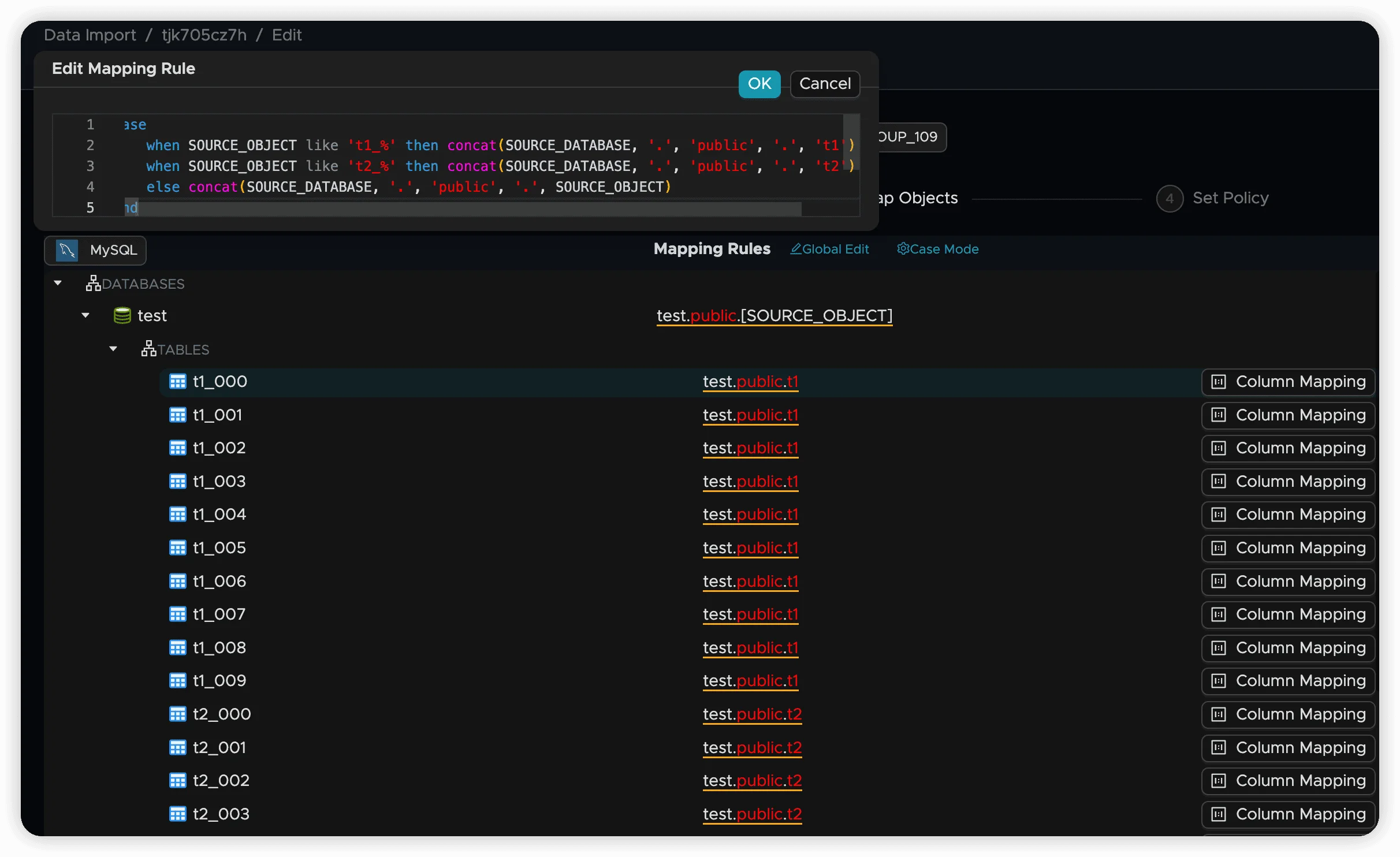
Using Regular Expressions:
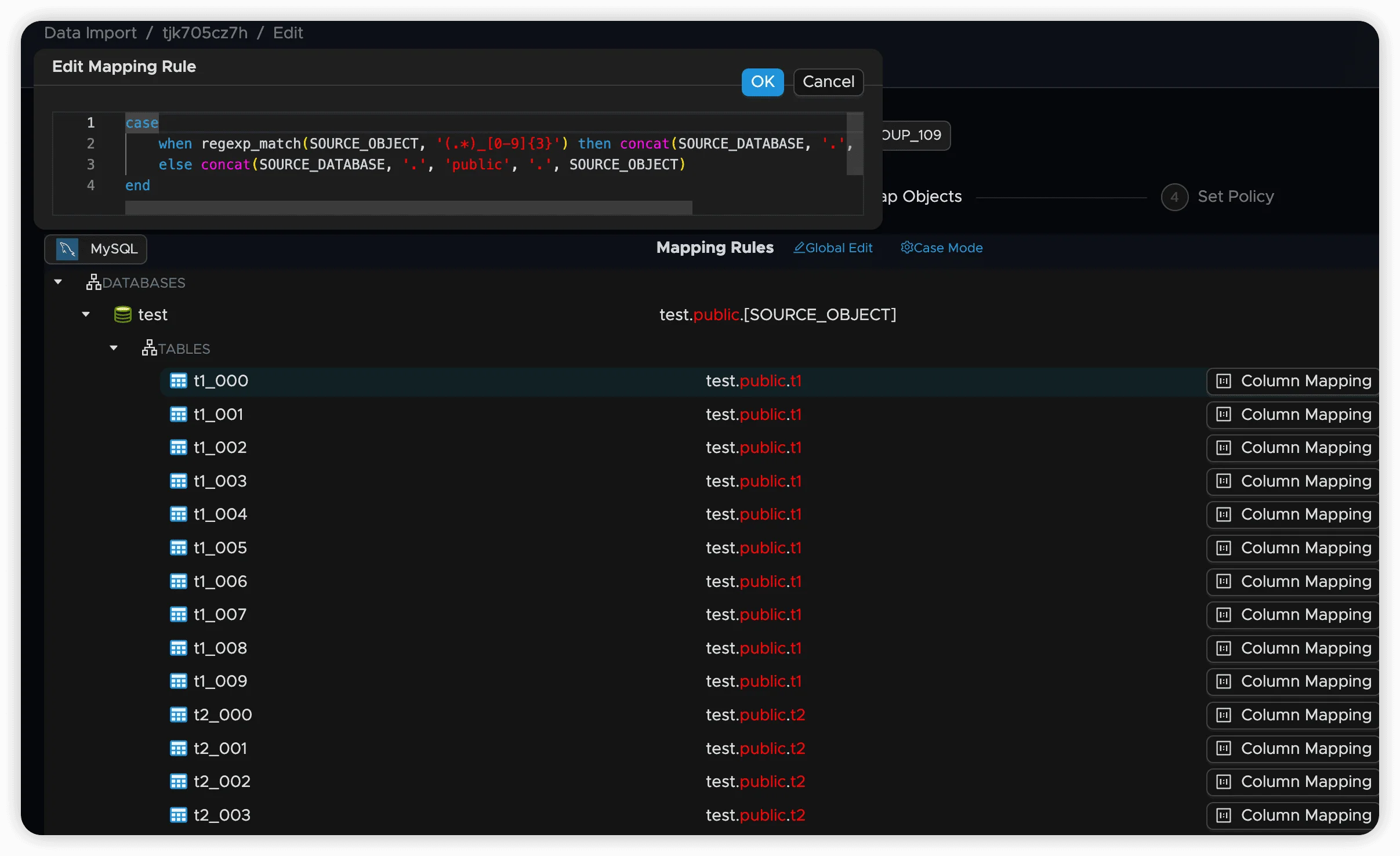
case
when regexp_match(SOURCE_OBJECT, '(.*)_[0-9]{3}$') then concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.', $1)
else concat(SOURCE_DATABASE, '.public.', SOURCE_OBJECT)
endThis pattern matches tables like users_001, users_002, etc., and maps them all to a single users table.
Column Mapping and Transformation
Configure field-level transformations including pruning, mapping, and type conversion.
Existing Target Tables
When the target table already exists, you can:
- Field Pruning: Select which source columns to include
- Field Mapping: Map source columns to different target column names
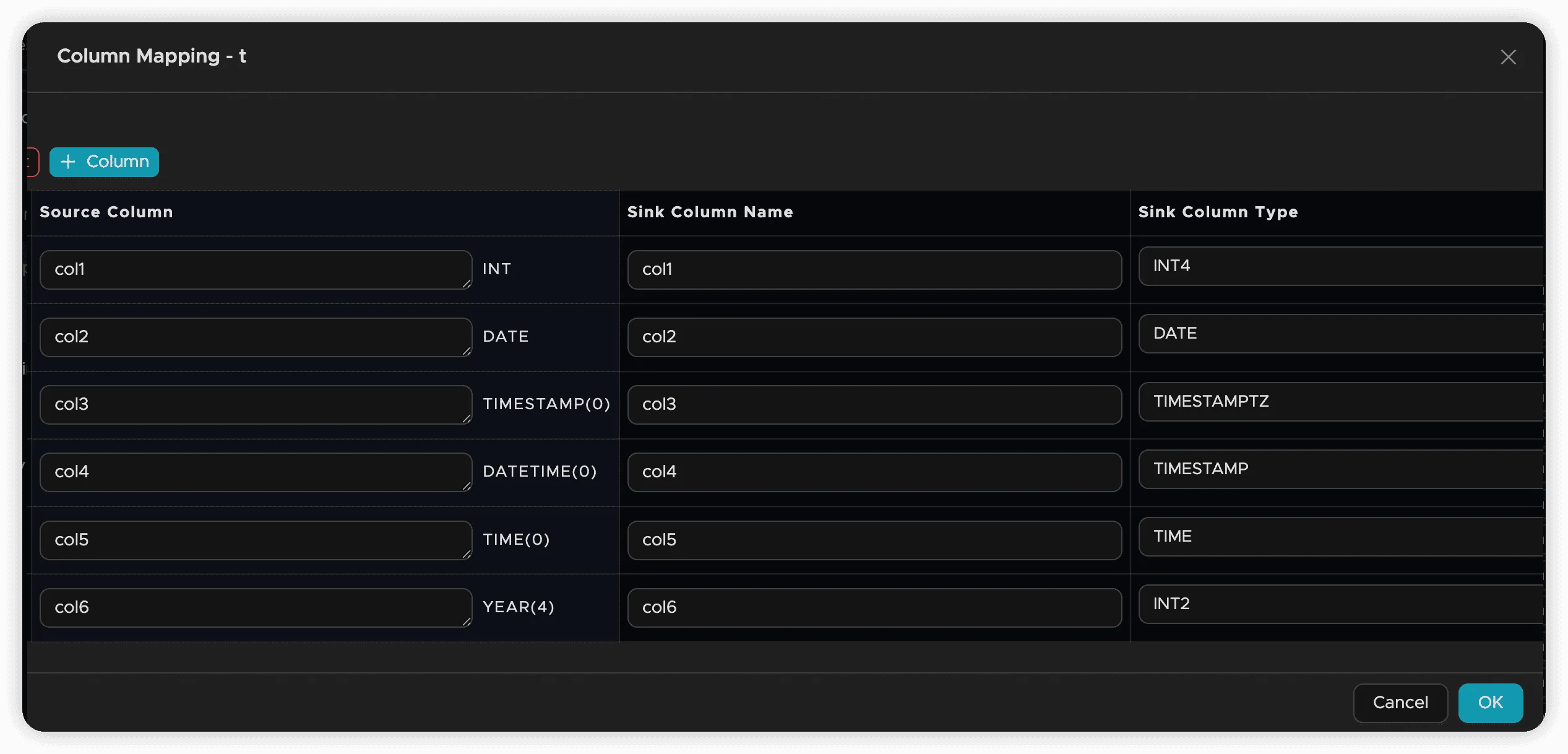
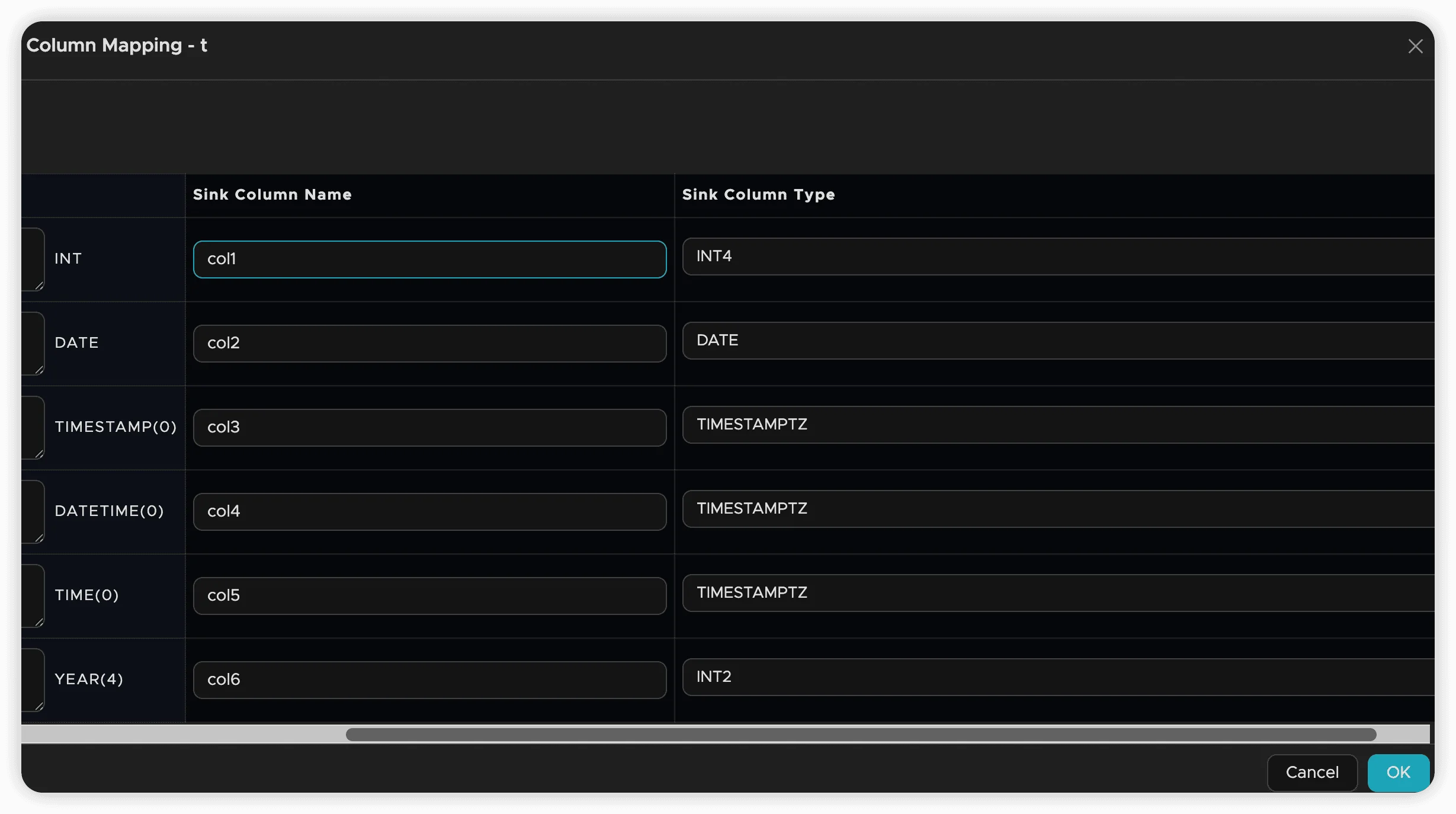
New Target Tables
When creating new target tables, additional options are available:
- Field Pruning: Select which source columns to include
- Field Renaming: Specify custom names for target columns
- Type Conversion: Change column data types during synchronization
Best Practices
- Start Simple: Begin with default mappings and customize as needed
- Test Patterns: Verify regex patterns match expected objects before deployment
- Plan for Scale: Design mapping rules that accommodate future growth
- Document Logic: Keep records of complex mapping rules for maintenance
- Use Descriptive Names: Choose clear, consistent naming conventions for target objects