Data Sync Edit Configs
Learn how to configure synchronization behavior in Data Sync. This guide covers DDL and DML operation settings, inheritance rules, and advanced configuration options.
Tacnode allows fine-grained control over synchronization behavior through object configuration settings. These settings determine which DDL (Data Definition Language) and DML (Data Manipulation Language) operations are synchronized from the source to the target.
Configuration Overview
During incremental synchronization, Data Sync filters operations based on object attributes. You can customize these attributes to:
- Control DDL Operations: Specify which schema changes to synchronize
- Filter DML Operations: Choose which data modifications to replicate
- Exclude Specific Behaviors: Prevent certain operations like deletions from being synchronized
Managing Configuration Settings
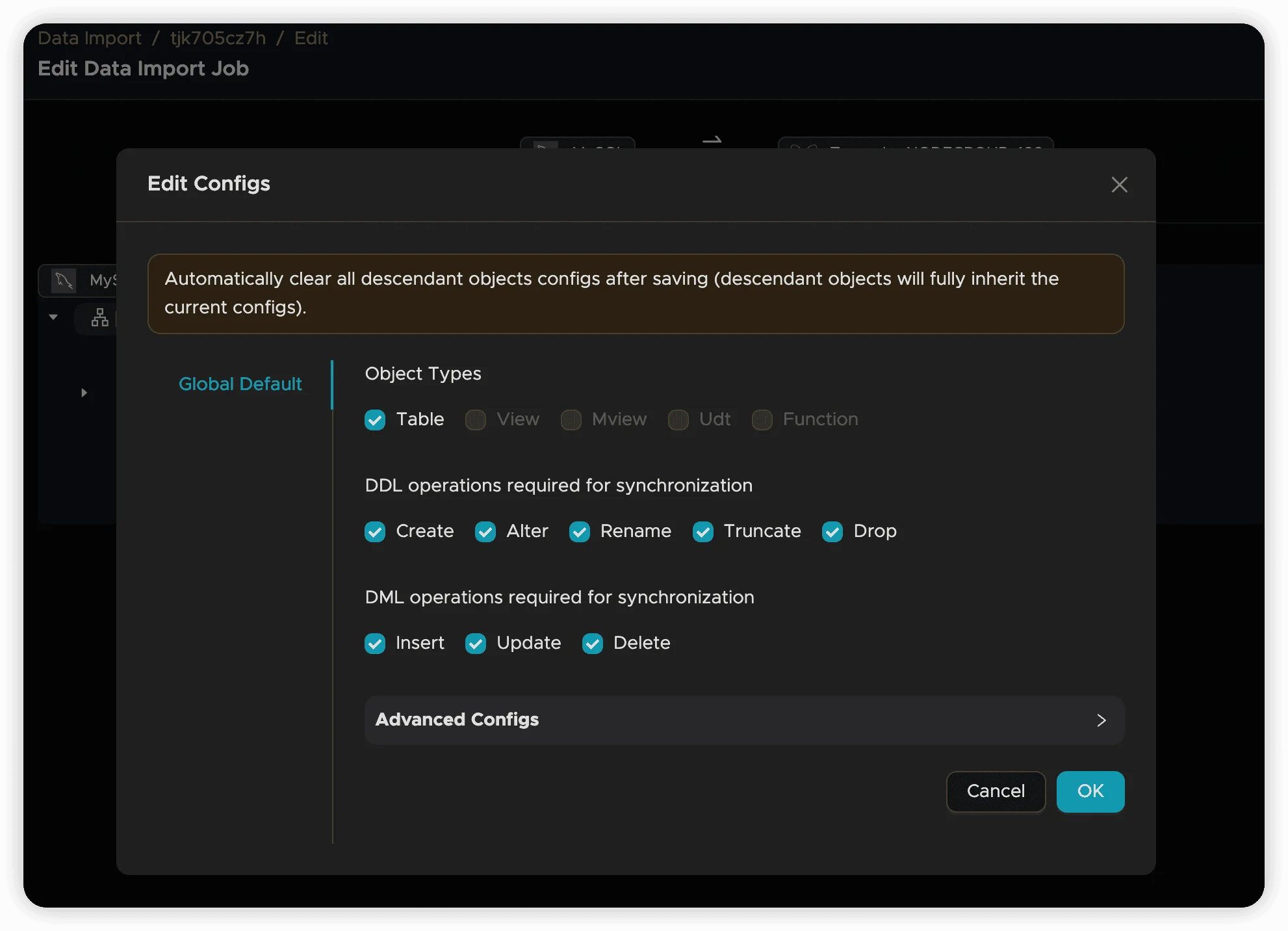
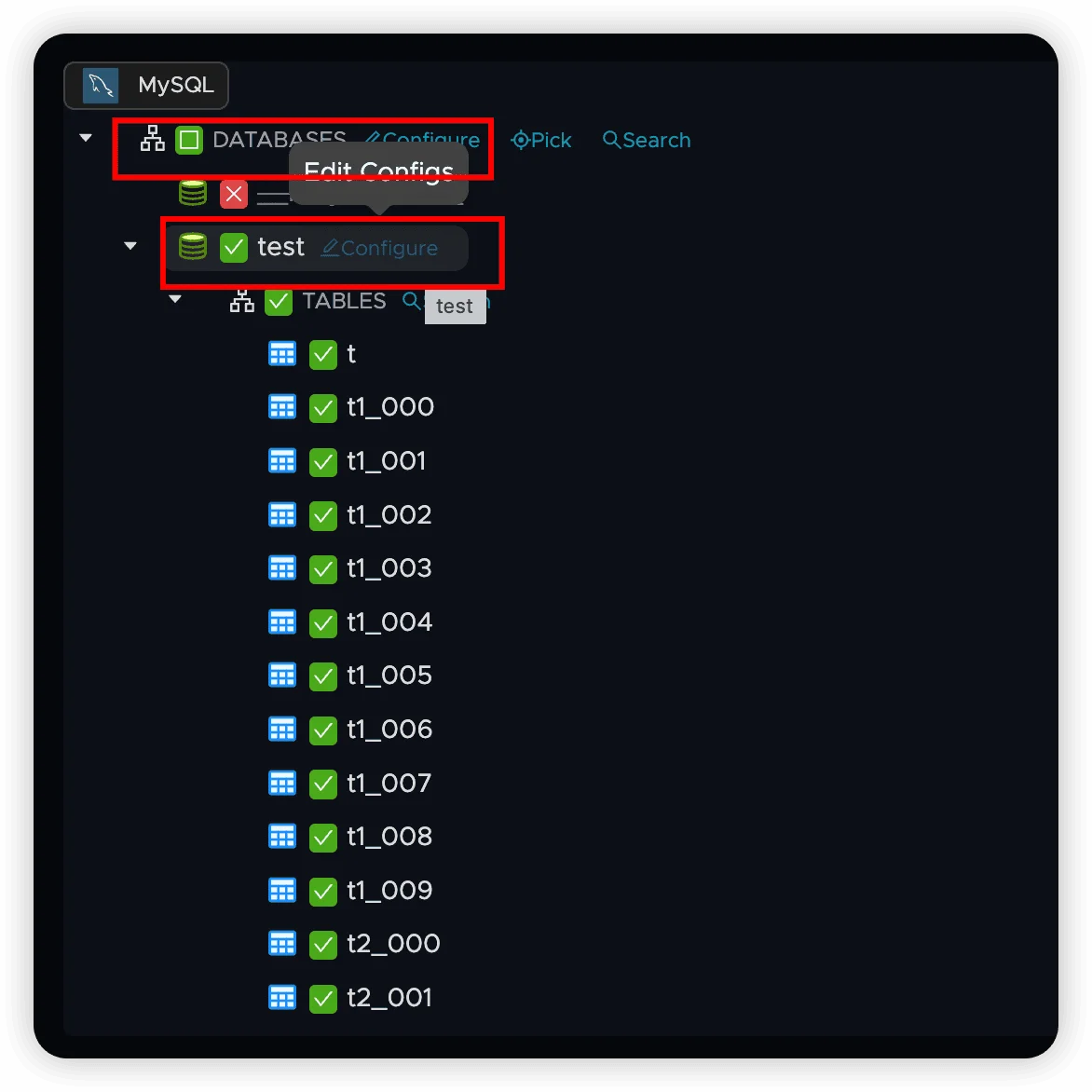
Access Configuration Options
Click the Configure button to modify global or node-specific properties.
Configuration Inheritance
Configuration follows a hierarchical inheritance model:
- Global Settings: Default configuration applied to all objects
- Node-Level Settings: Override global settings for specific nodes
- Child Inheritance: Child nodes automatically inherit parent configurations
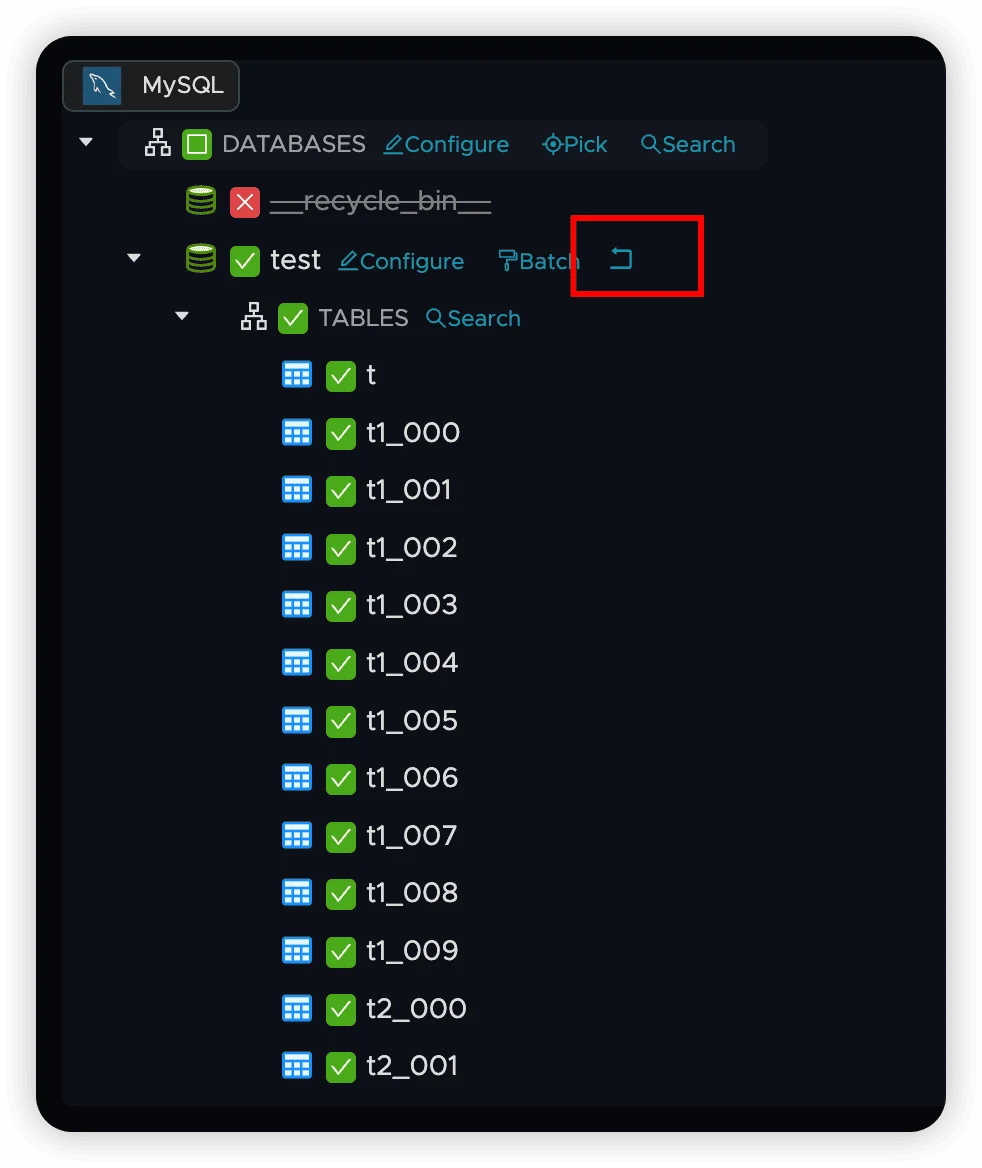
Reverting Changes
When node-specific attributes are set, an Undo button appears (highlighted in red). Click this button to:
- Remove node-specific settings
- Restore parent node or global attributes
- Return to inherited configuration
Configuration Attributes
DDL Operations
Control which schema changes are synchronized:
Create Operations
- Description: Synchronize new table creation
- Default: Enabled
- Use Case: Automatically replicate new tables as they’re added to the source
Alter Operations
- Description: Synchronize table modifications (currently supports adding fields only)
- Default: Enabled
- Limitations: Only field additions are currently supported
- Use Case: Keep table schemas synchronized as they evolve
Rename Operations
- Description: Synchronize table and column rename operations
- Default: Disabled
- Use Case: Maintain naming consistency between source and target
Truncate Operations
- Description: Synchronize table truncation (remove all data)
- Default: Disabled
- Use Case: Replicate bulk data removal operations
Drop Operations
- Description: Synchronize table deletion
- Default: Disabled
- Use Case: Remove tables from target when deleted from source
DML Operations
Control which data changes are synchronized:
Insert Operations
- Description: Synchronize new record additions
- Default: Enabled
- Use Case: Replicate all new data from source to target
Update Operations
- Description: Synchronize record modifications
- Default: Enabled
- Use Case: Keep existing records synchronized between systems
Delete Operations
- Description: Synchronize record deletions
- Default: Enabled
- Use Case: Remove records from target when deleted from source
Lossless Schema Changes
When using schema change management tools, you can enable Lossless Schema Changes mode. In this mode, these tools typically:
- Create Temporary Tables: Generate temporary tables for schema modifications
- Data Migration: Copy data to temporary tables
- Schema Application: Apply changes to temporary tables
- Table Replacement: Use RENAME operations to replace original tables
DataSync supports this workflow when Create, Alter, Drop, and Rename operations are enabled. However, in certain scenarios, this approach may not be suitable:
- Fixed Table Synchronization: When sync jobs target specific tables and don’t monitor new table creation
- Dependency Constraints: When target tables have view dependencies that prevent RENAME operations
- Production Stability: When avoiding temporary table creation is preferred
Enabling Lossless Schema Changes
Benefits of Lossless Mode:
- No Temporary Tables: Bypasses temporary table creation entirely
- Direct Application: Leverages Tacnode’s native Online Schema Evolution capabilities
- Table ID Preservation: Maintains table identifiers without changes
- View Compatibility: No need to rebuild dependent views
- Reduced Complexity: Simplifies schema change workflow
How Lossless Schema Changes Work
Instead of the traditional temporary table approach:
-- Traditional approach (with temporary tables)
CREATE TABLE temp_users_new AS SELECT * FROM users;
ALTER TABLE temp_users_new ADD COLUMN email VARCHAR(255);
-- Data migration and validation
RENAME TABLE users TO users_backup, temp_users_new TO users;
-- Lossless approach (direct application)
ALTER TABLE users ADD COLUMN email VARCHAR(255);
-- Changes applied directly using Online Schema EvolutionTechnical Implementation:
- Schema Analysis: DataSync analyzes the proposed schema changes
- Compatibility Check: Verifies changes are compatible with Online Schema Evolution
- Direct Application: Applies changes directly to the target table
- Transaction Safety: Ensures changes are applied atomically
Use Cases for Lossless Schema Changes
Recommended Scenarios:
- Production environments with strict change control
- Systems with complex view dependencies
- High-availability requirements with minimal downtime
- Large tables where temporary copies would be resource-intensive
Configuration Example:
{
"table_config": {
"users": {
"ddl_operations": {
"create": true,
"alter": true,
"drop": false,
"rename": false
},
"lossless_schema_changes": true,
"online_schema_evolution": {
"enable_parallel_execution": true,
"max_lock_time": "30s",
"progress_monitoring": true
}
}
}
}Limitations and Considerations
Current Limitations:
- Requires compatible schema changes (additive operations work best)
- Some complex schema modifications may still require traditional approach
- Performance impact during large table modifications
Best Practices:
-- Monitor schema change progress
SELECT
schemaname,
tablename,
operation_type,
progress_percent,
estimated_completion
FROM pg_stat_progress_alter_table;
-- Verify schema change completion
SELECT
table_name,
column_name,
data_type,
is_nullable
FROM information_schema.columns
WHERE table_name = 'target_table'
ORDER BY ordinal_position;Advanced Configuration
Access additional settings through the Advanced Configs section:
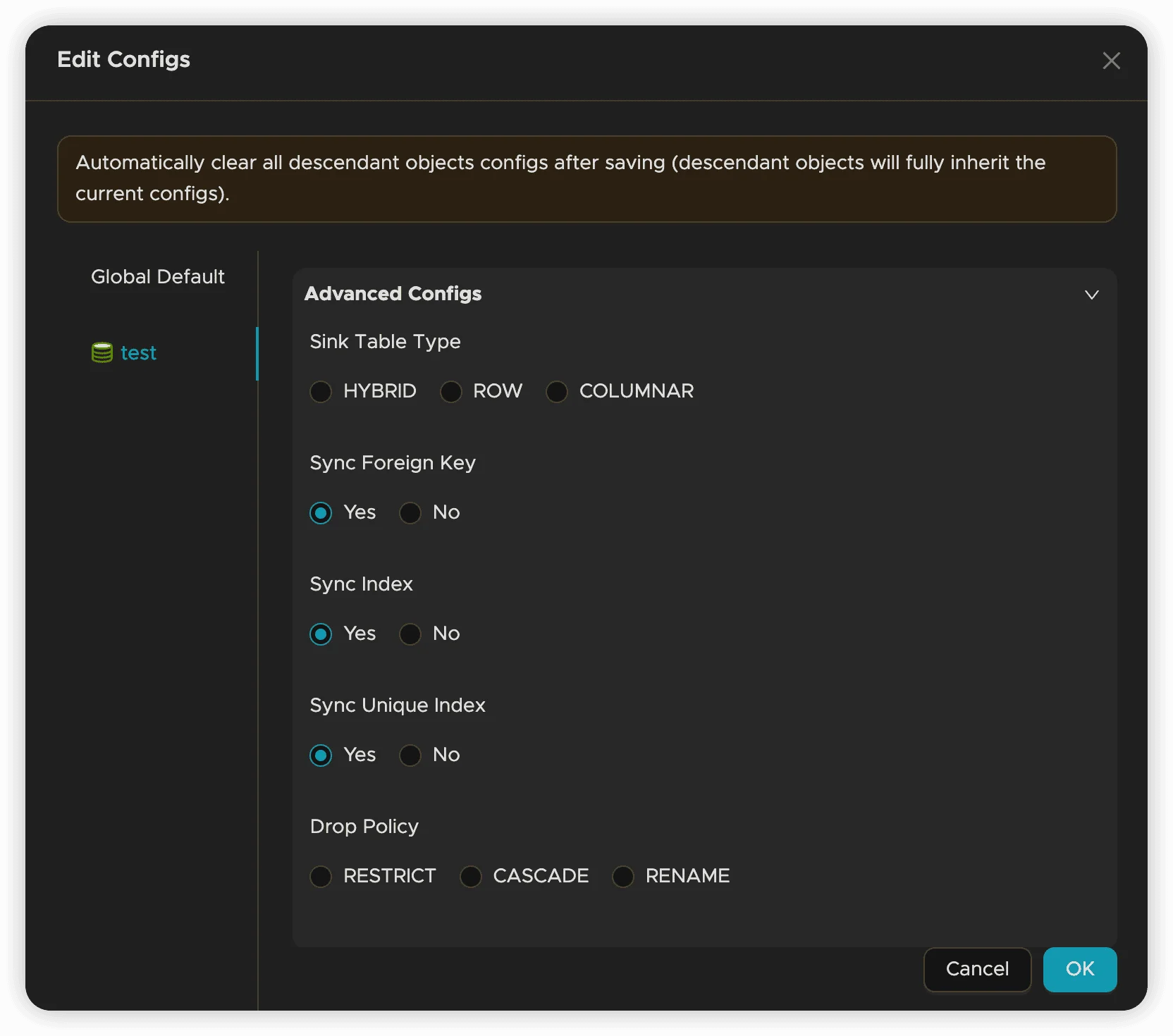
Advanced options may include:
- Batch Size: Control how many operations are processed together
- Retry Policies: Configure error handling and retry behavior
- Conflict Resolution: Define how to handle conflicting changes
- Performance Tuning: Optimize synchronization performance parameters
Common Configuration Scenarios
Scenario 1: Read-Only Replication
For read-only replicas, you might configure:
- DDL: Enable Create and Alter only
- DML: Enable Insert and Update only (disable Delete)
This ensures data is added and updated but never removed from the target.
Scenario 2: Schema Synchronization Only
For schema-only synchronization:
- DDL: Enable all operations
- DML: Disable all operations
This keeps table structures synchronized without replicating data.
Scenario 3: Audit Trail Preservation
For maintaining complete audit trails:
- DDL: Enable Create and Alter only
- DML: Enable Insert and Update only (disable Delete)
This preserves historical data while keeping current information synchronized.
Best Practices
Planning Configuration
- Understand Requirements: Identify which operations your use case requires
- Start Conservative: Begin with minimal permissions and add as needed
- Test Configuration: Verify settings work as expected in a test environment
Managing Inheritance
- Use Global Defaults: Set sensible global defaults for most use cases
- Override Selectively: Only override settings for nodes that need different behavior
- Document Exceptions: Keep track of nodes with custom configurations
Monitoring and Maintenance
- Regular Review: Periodically review configuration settings
- Monitor Impact: Watch for unexpected behavior after configuration changes
- Version Control: Track configuration changes for rollback purposes