Backup and Restore
Learn how to efficiently backup and restore your Tacnode databases with comprehensive guides for data protection and disaster recovery.
Database backup creates copies of your data and metadata to protect against accidental deletions, hardware failures, software issues, and disasters. Restore operations recover your database from these backups to return to a previous state.
Tacnode provides robust database-level backup and recovery capabilities with automated scheduling and configurable retention policies.
Understanding Backup Operations
What Gets Backed Up
- All database tables and indexes
- Database schema and metadata
- User permissions and roles
- Transaction logs up to the backup point
Backup Types
- Full Backup: Complete database snapshot
- Automated Backups: Scheduled backups with configurable retention
- Manual Backups: On-demand backups for specific events
Creating Database Backups
Prerequisites
- Database must be in “Attached” state
- Proper permissions for backup operations
- Sufficient storage quota for backup files
Step-by-Step Backup Process
-
Navigate to your Context Lake
- From the console home page, enter your Context Lake environment
-
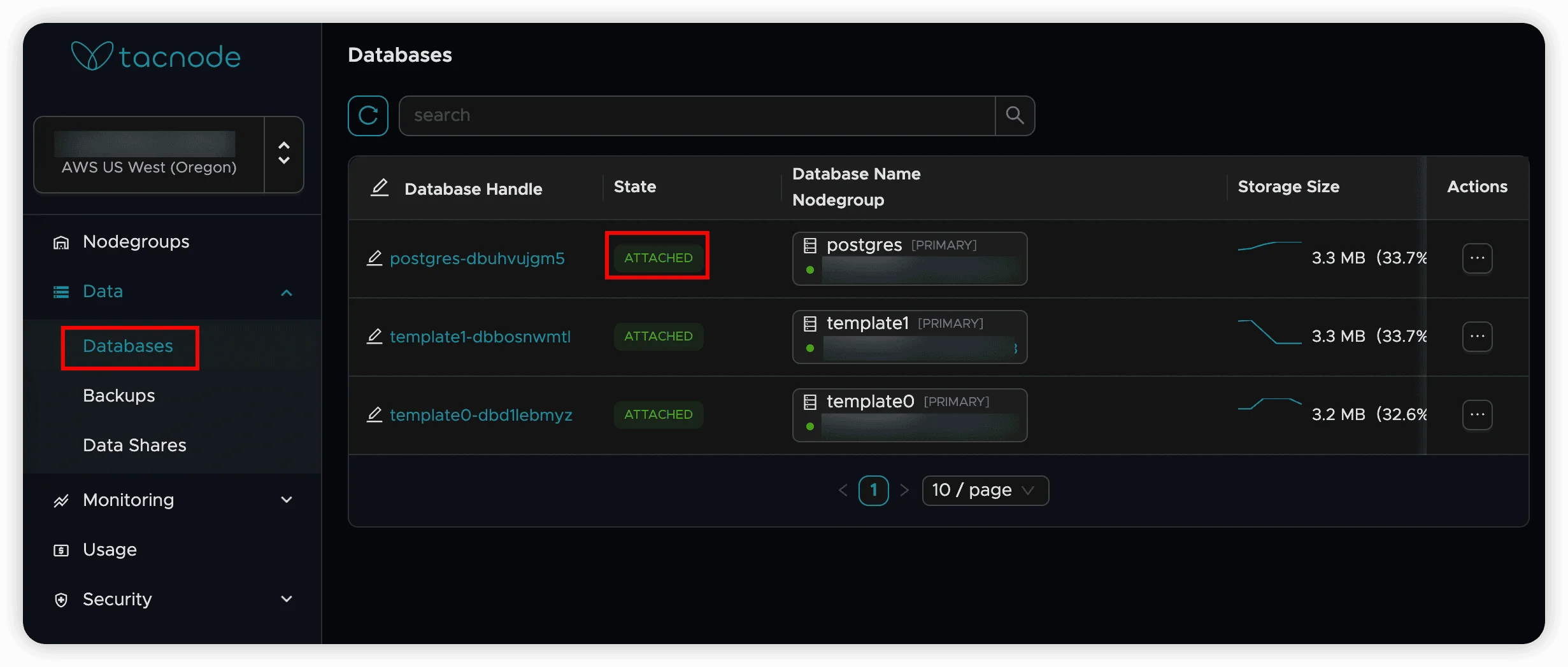
Locate the Target Database
- Go to “Data” → “Database” tab
- Find the database you want to backup
- Verify it shows “Attached” status
-
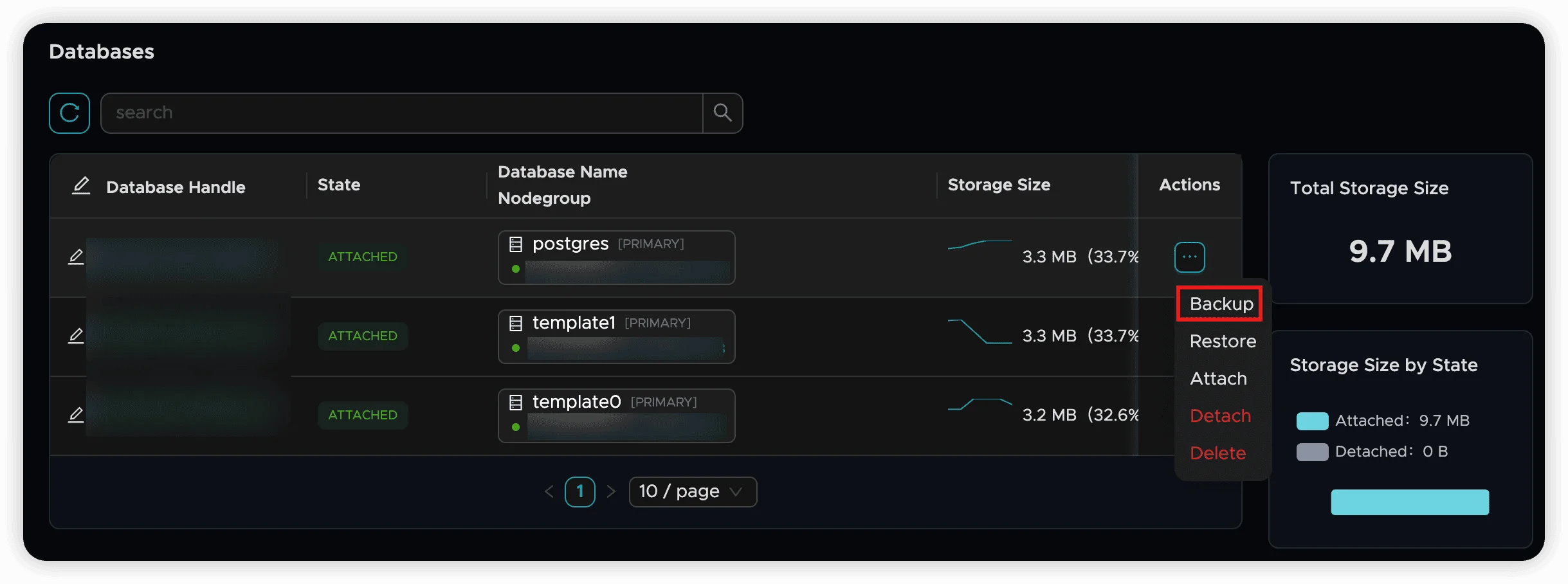
Initiate Backup
- Click the “Backup” button for your target database
-
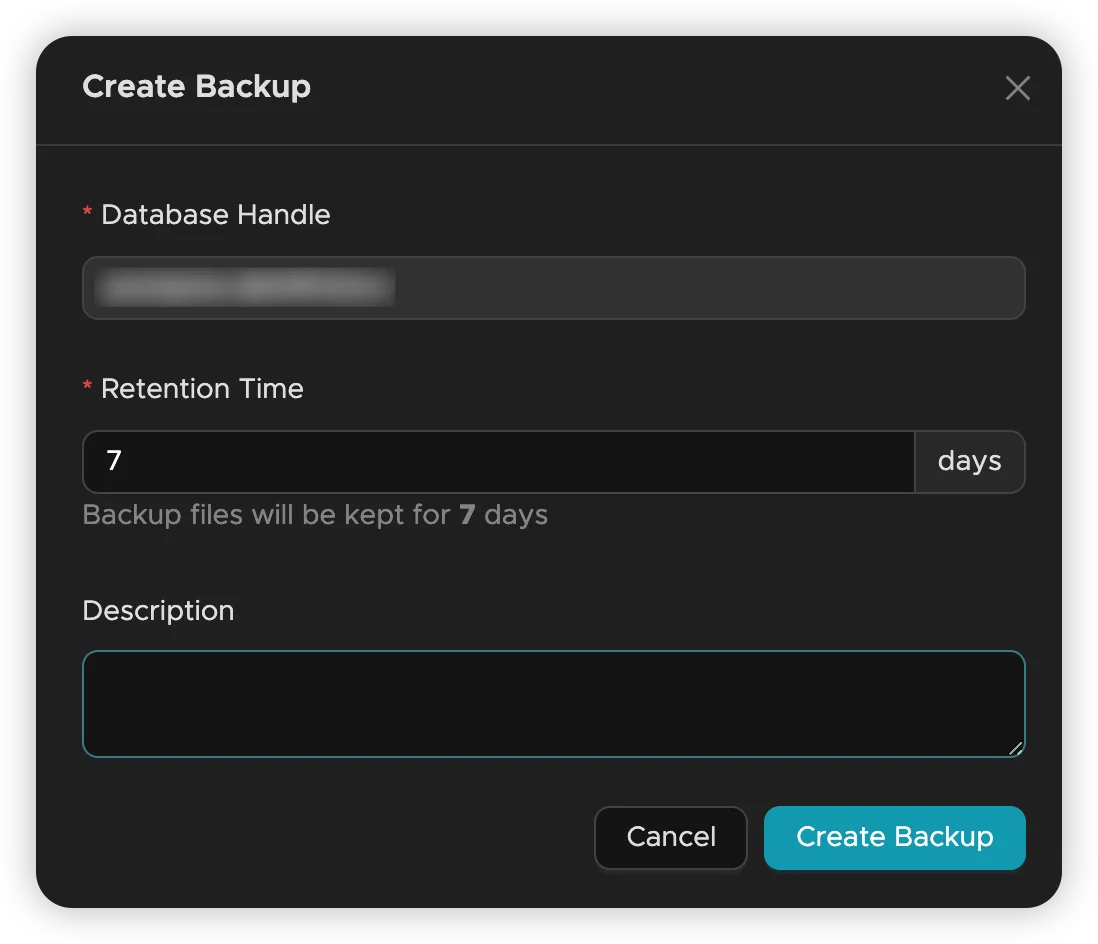
Configure Backup Settings
- Retention Period: Set how long to keep the backup (required)
- Description: Add optional notes about this backup
- Click “OK” to start the backup process
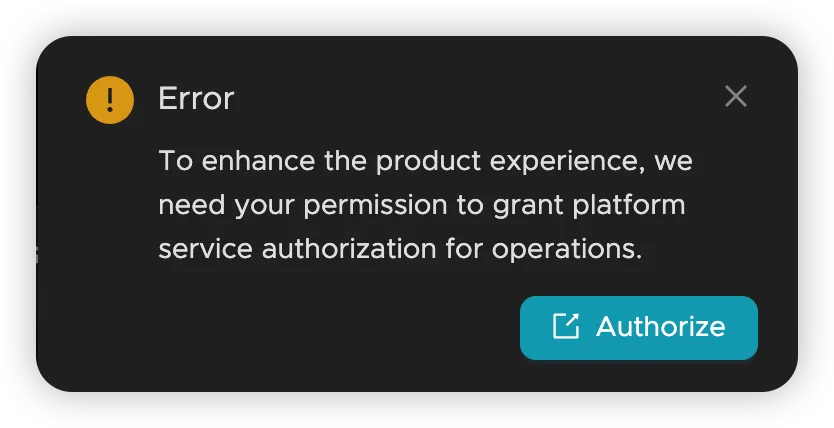
- Authorize the backup operation when prompted (first-time setup)
-
Monitor Backup Progress
- Backup runs asynchronously in the background
- Check the “Backup files” list for task status
- Successful backups appear in the backup inventory
Managing Backup Files
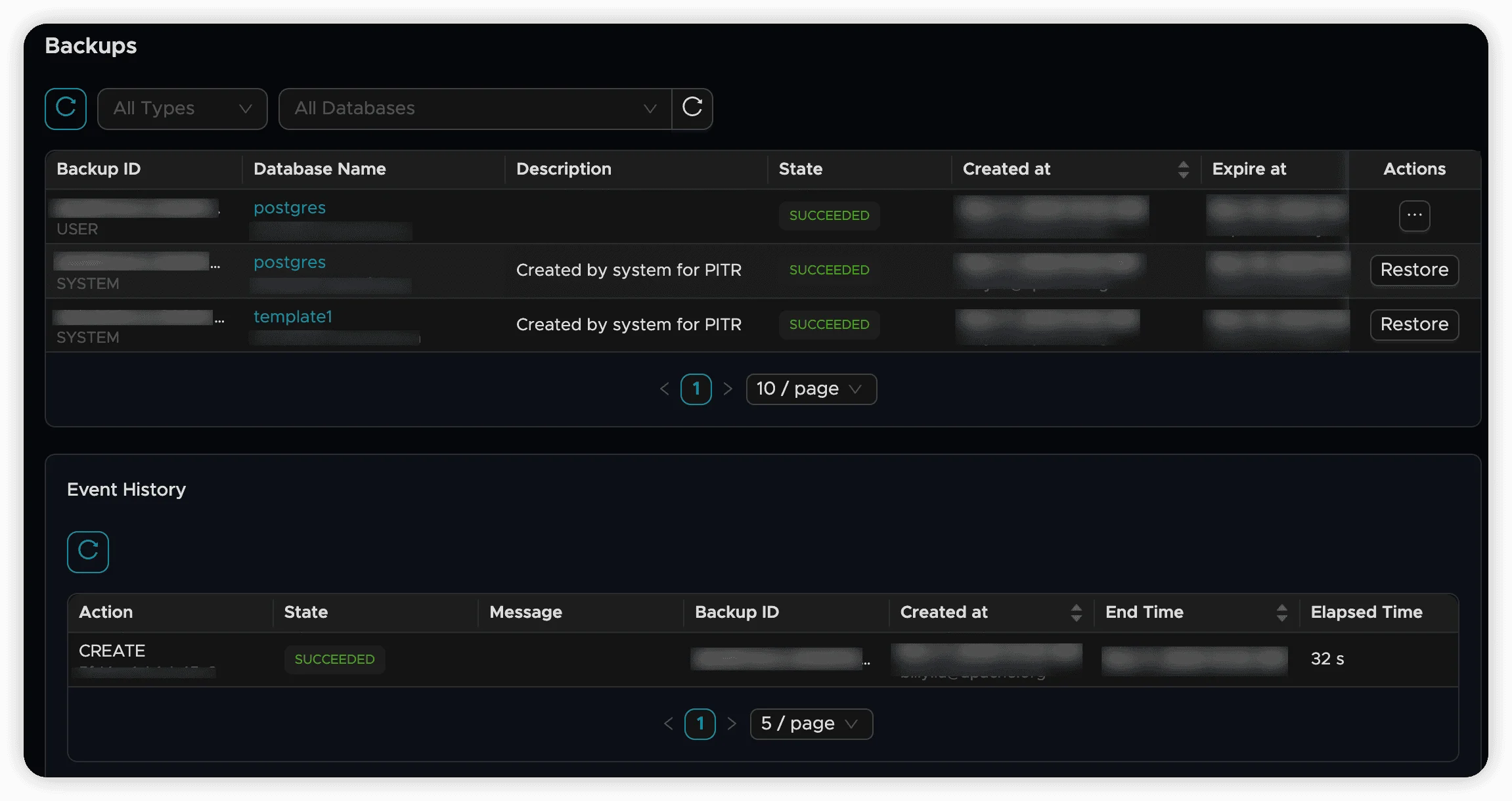
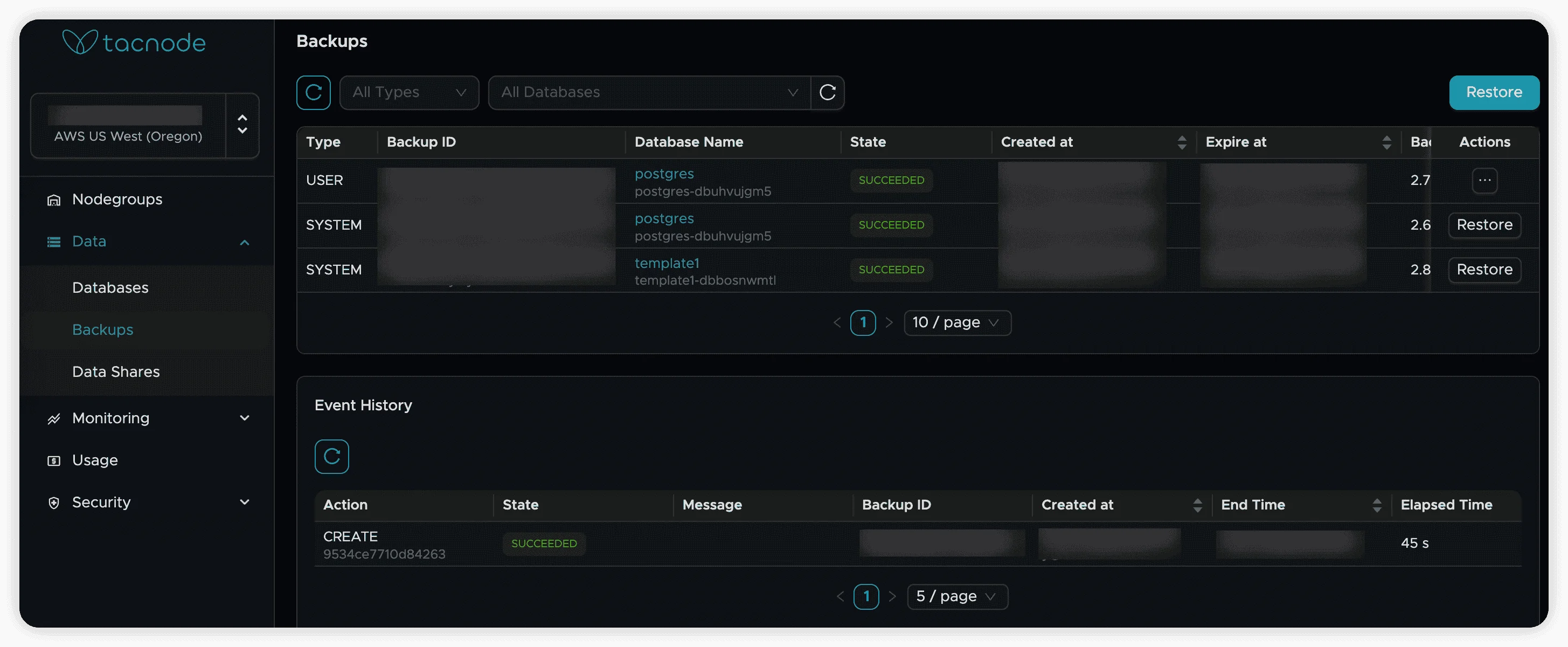
Viewing Available Backups
- Navigate to the “Backup” tab in your Context Lake
- View all completed backups and current backup tasks
- Monitor backup job status and completion times
Backup File Information
Each backup entry displays:
- Source database name
- Backup creation timestamp
- File size and retention period
- Backup status and description
Restoring from Backups
When to Use Restore
- Recover from accidental data deletion
- Restore corrupted databases
- Clone databases for testing or development
- Migrate data between environments
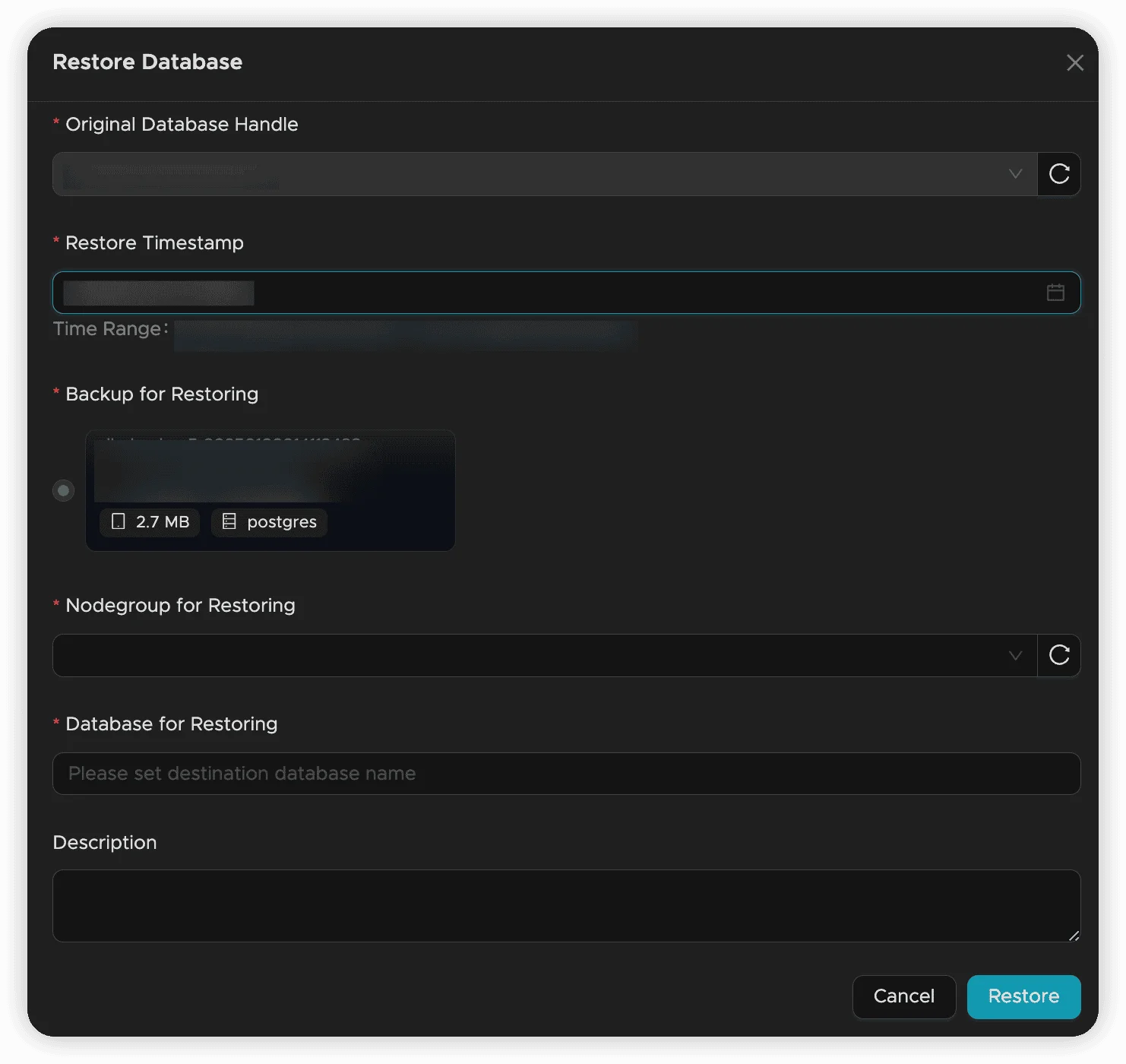
Restore Process
-
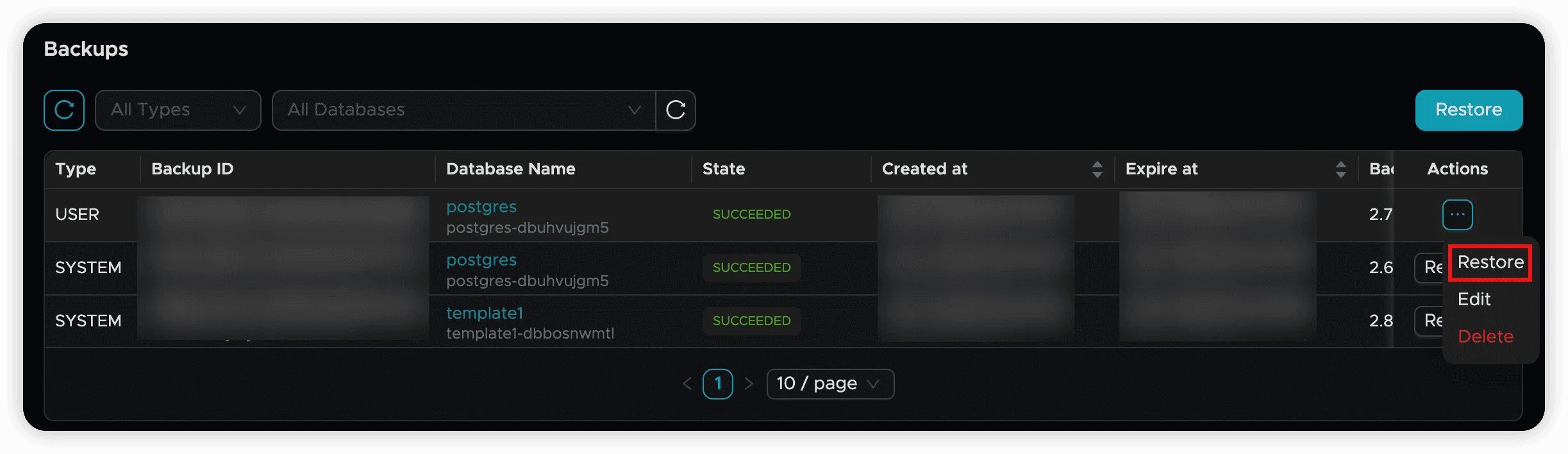
Select Backup File
- Locate the backup you want to restore from
- Click the “Restore” button
-
Configure Restore Settings
- Target Database Name: Specify the restored database name
- Nodegroup: Choose where to perform the restore
- Description: Add optional notes about this restore operation
- Click “OK” to start restoration
-
Monitor Restore Progress
- Restore operations run asynchronously
- Check task status on the Backup page
- Restoration creates a new database instance

-
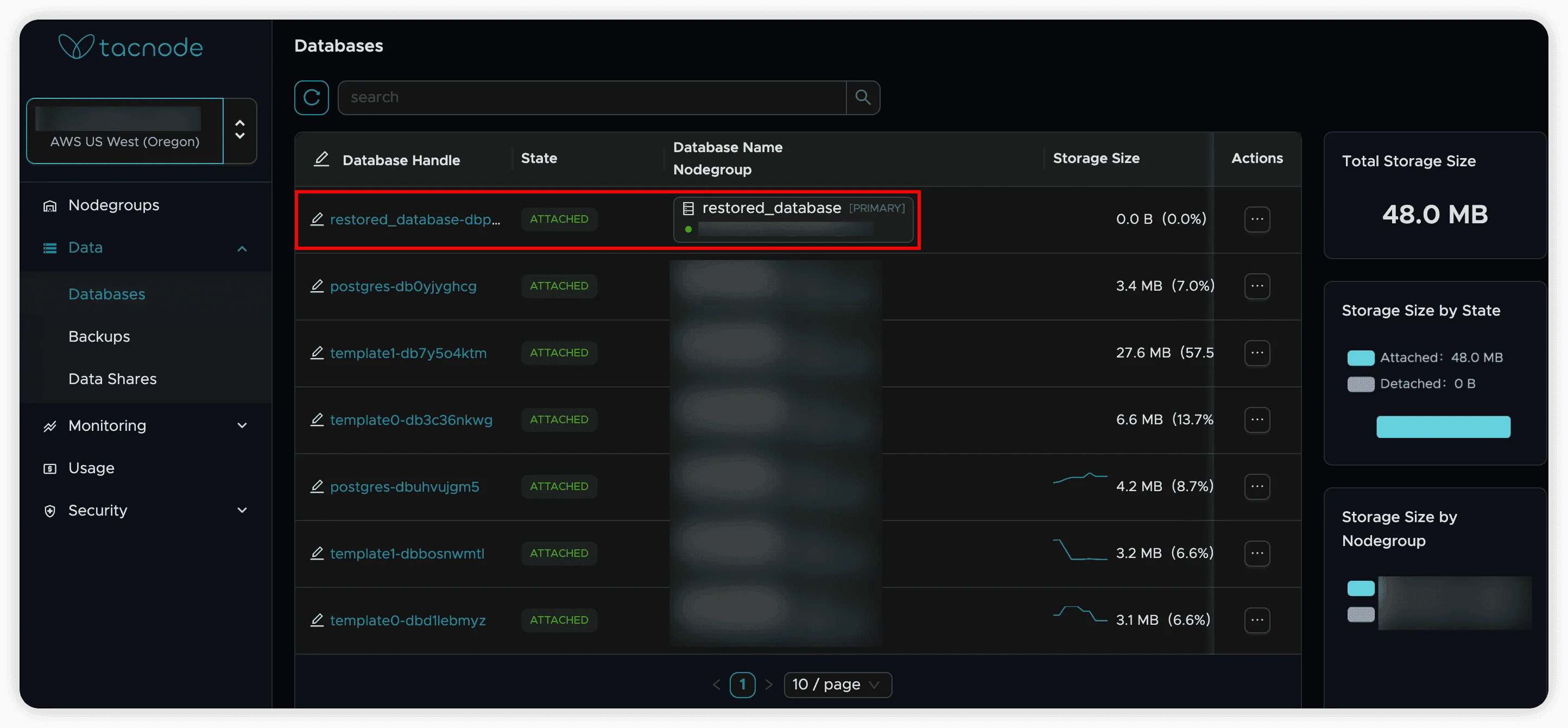
Verify Restored Database
- Once complete, find the restored database in the “Database” tab
- Database is automatically attached to the nodegroup that performed the restore
- Verify data integrity and accessibility
Best Practices
Backup Strategy
- Regular Schedule: Set up automated daily backups for production databases
- Retention Policy: Balance storage costs with recovery requirements
- Test Restores: Regularly test restore procedures to ensure backup integrity
- Documentation: Maintain clear naming conventions and descriptions
Security Considerations
- Backup files inherit the same security policies as source databases
- Ensure proper access controls for backup management operations
- Monitor backup and restore activities through audit logs
Performance Impact
- Backups have minimal impact on database performance
- Schedule large backups during low-activity periods when possible
- Monitor storage usage to avoid quota exhaustion
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Backup Fails: Check database status and permissions
- Insufficient Storage: Verify backup storage quotas
- Authorization Required: Complete first-time backup authorization
- Restore Fails: Ensure target nodegroup has sufficient resources
Getting Help
If you encounter persistent issues with backup or restore operations, contact Tacnode support with:
- Database and backup identifiers
- Error messages and timestamps
- Current system status and configuration