Third-Party MCP Server
Learn how to connect popular open-source MCP servers to Tacnode, including server-postgres and DBHub for enhanced AI and database integration.
Tacnode’s PostgreSQL compatibility enables seamless integration with the broader Model Context Protocol (MCP) ecosystem. This guide demonstrates how to connect popular third-party MCP servers to Tacnode and validate functionality using debugging tools.
MCP Architecture Overview
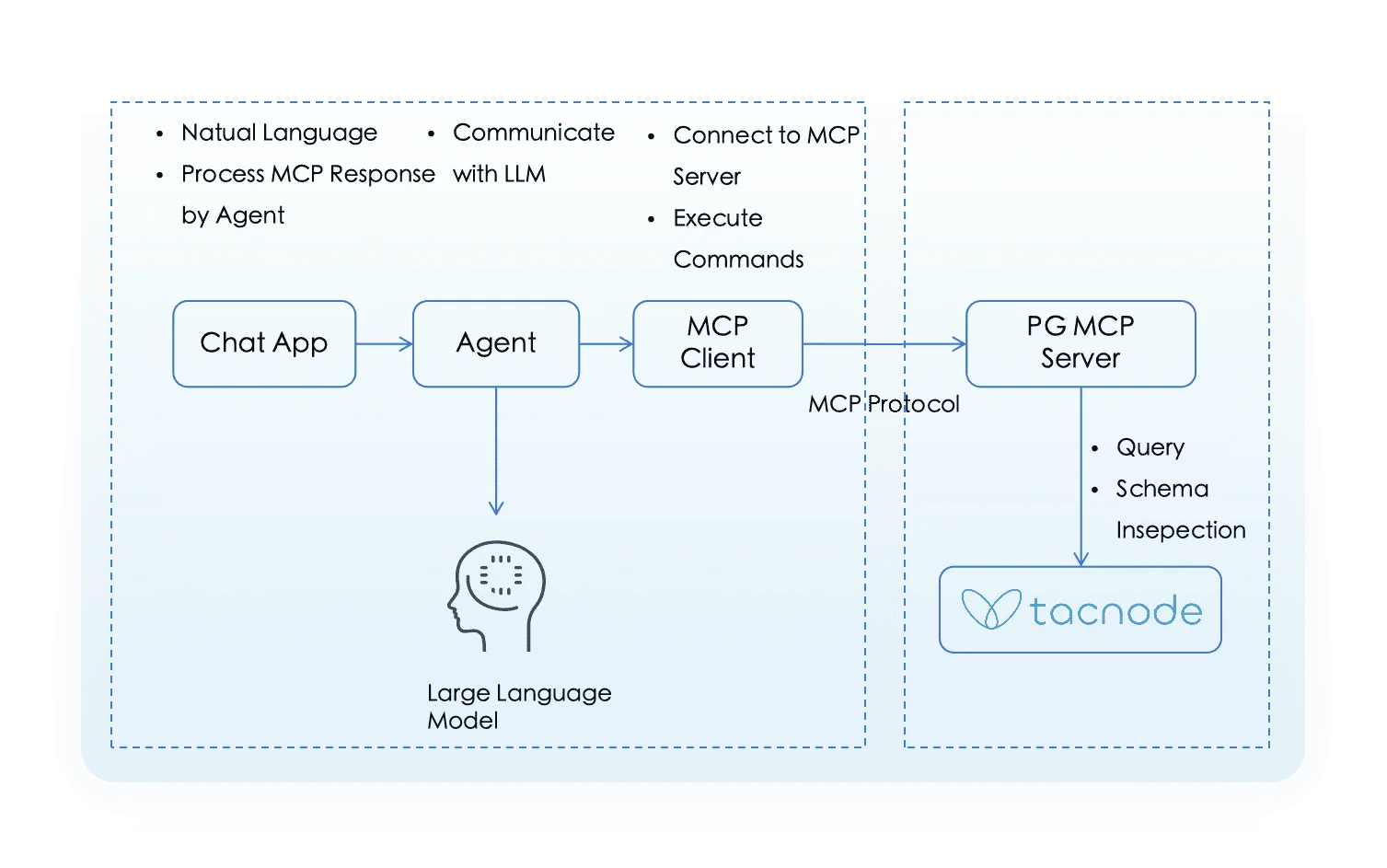
MCP servers form part of a larger service chain that connects databases to AI agents and large language models. In this architecture:
- MCP Server: Provides data query and schema exploration capabilities (e.g., server-postgres, DBHub)
- MCP Client: Interface for testing and interaction (e.g., MCP Inspector, Claude Desktop)
- Large Language Models: AI systems that consume the data (e.g., ChatGPT, DeepSeek, Gemini)
This guide focuses on MCP Client and MCP Server interactions, without covering LLM integration.
MCP Inspector
MCP Inspector is a visual testing tool designed for the Model Context Protocol ecosystem. It provides standardized data structures and protocols for AI environments, enabling plug-and-play LLM contexts with cross-platform traceability.
Key Features
- Cross-platform visualization: Comprehensive tracking of prompts, results, environments, and reference chains
- Multi-platform support: Compatible with browser, IoT, and server-side AI contexts
- Standardized protocol: Simplified data structures for easy integration and testing
- Transparency: Enhanced visibility into prompt engineering, context data, and plugin interactions
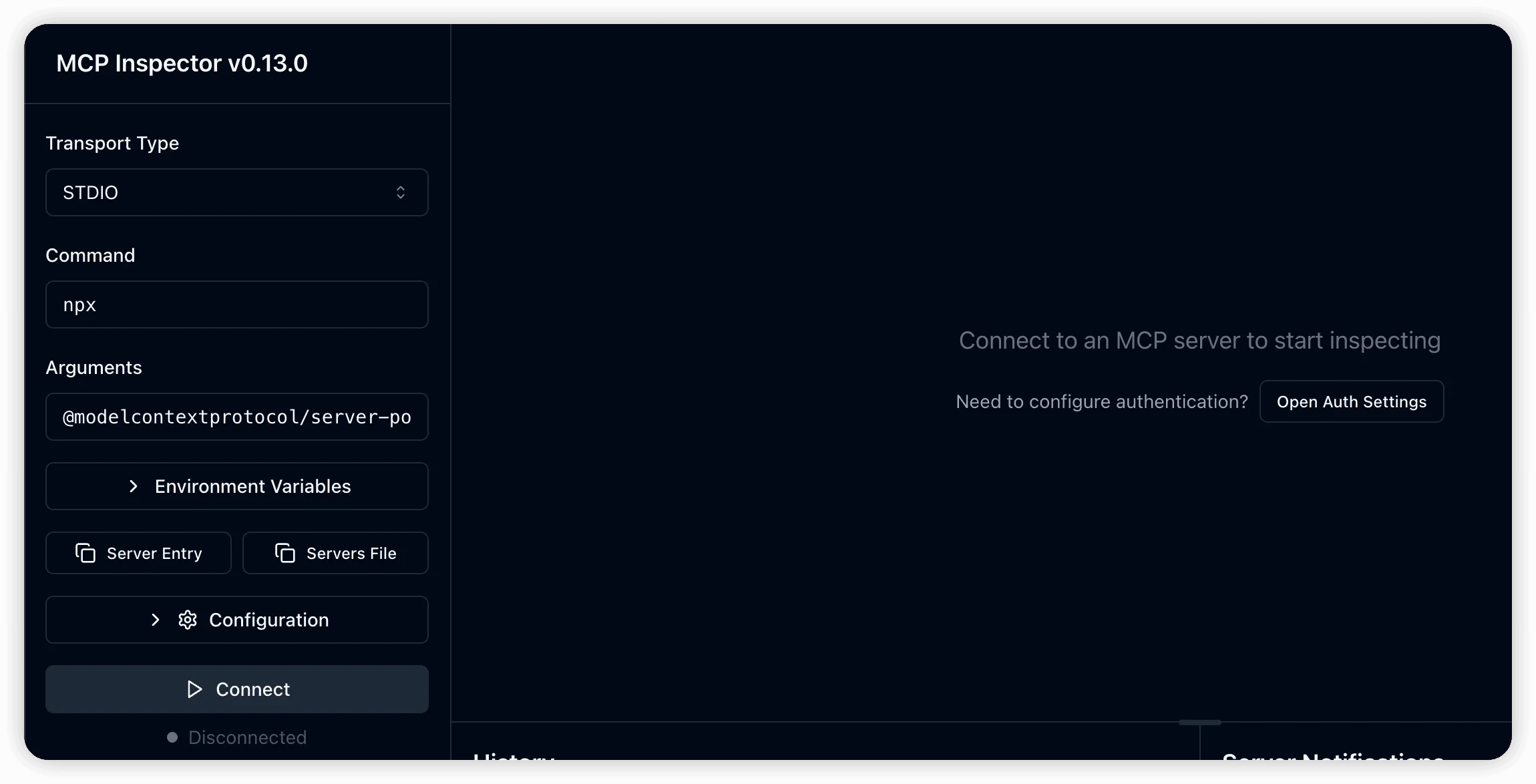
Starting MCP Inspector
Launch MCP Inspector using npx for quick setup:
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspectorThis opens the MCP Inspector interface in your browser:
Official PostgreSQL MCP Server
The official server-postgres is the reference PostgreSQL implementation within the MCP ecosystem. It provides standardized APIs for database interaction while maintaining strict read-only access for security.
Repository: modelcontextprotocol/servers
Key Features
- Read-only database queries for secure data access
- Table metadata retrieval for schema exploration
- STDIO transport protocol for local communication
- PostgreSQL wire protocol compatibility
Connecting server-postgres to Tacnode
Launch the PostgreSQL MCP server directly through MCP Inspector:
Configuration Parameters:
- Transport Protocol: STDIO
- Command:
npx - Arguments:
@modelcontextprotocol/server-postgres - Connection String:
postgres://username:password@host:port/database
Available Operations
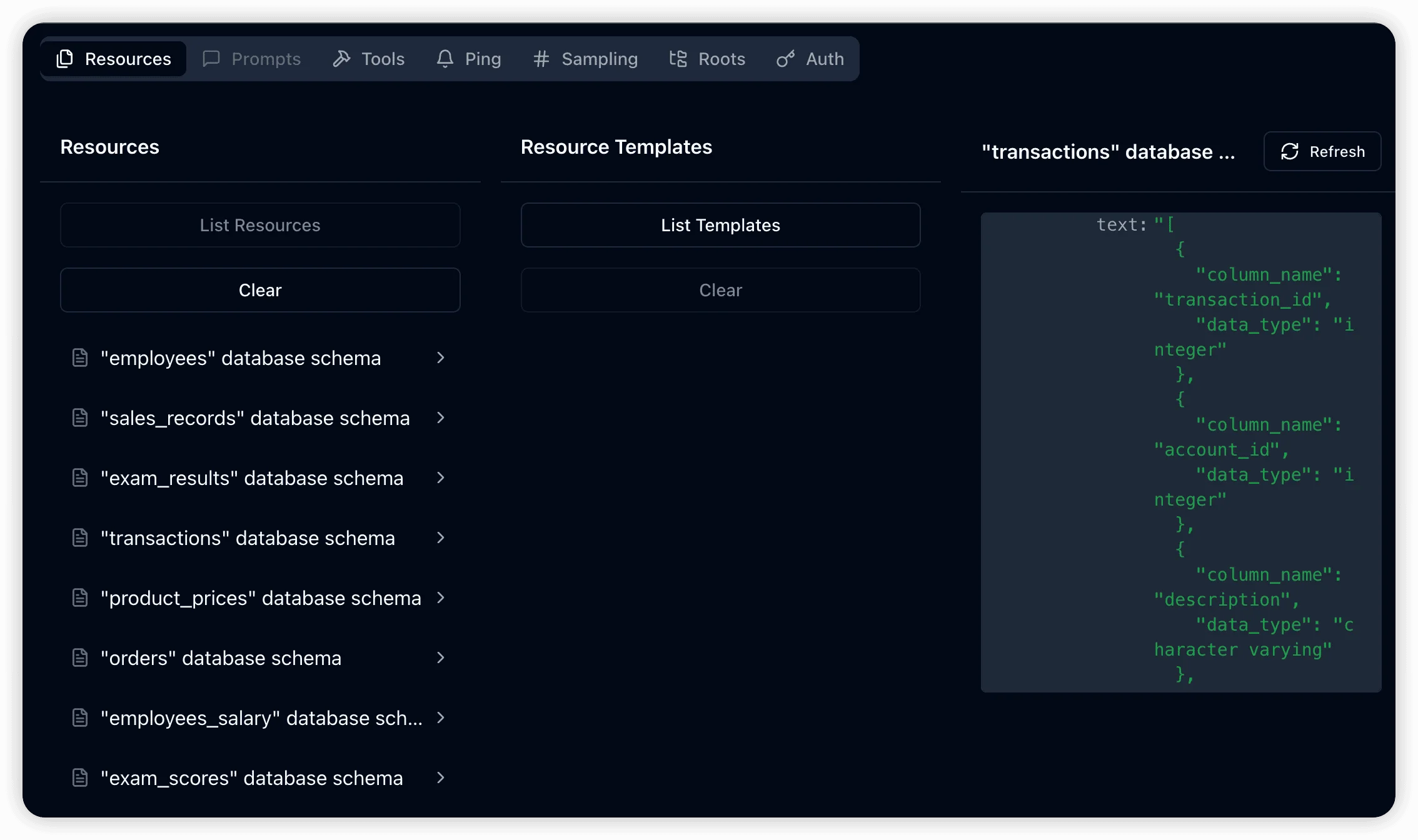
Resource Management:
resources/list: Enumerate all available tables and return metadataresources/read: Retrieve detailed metadata for specific tables
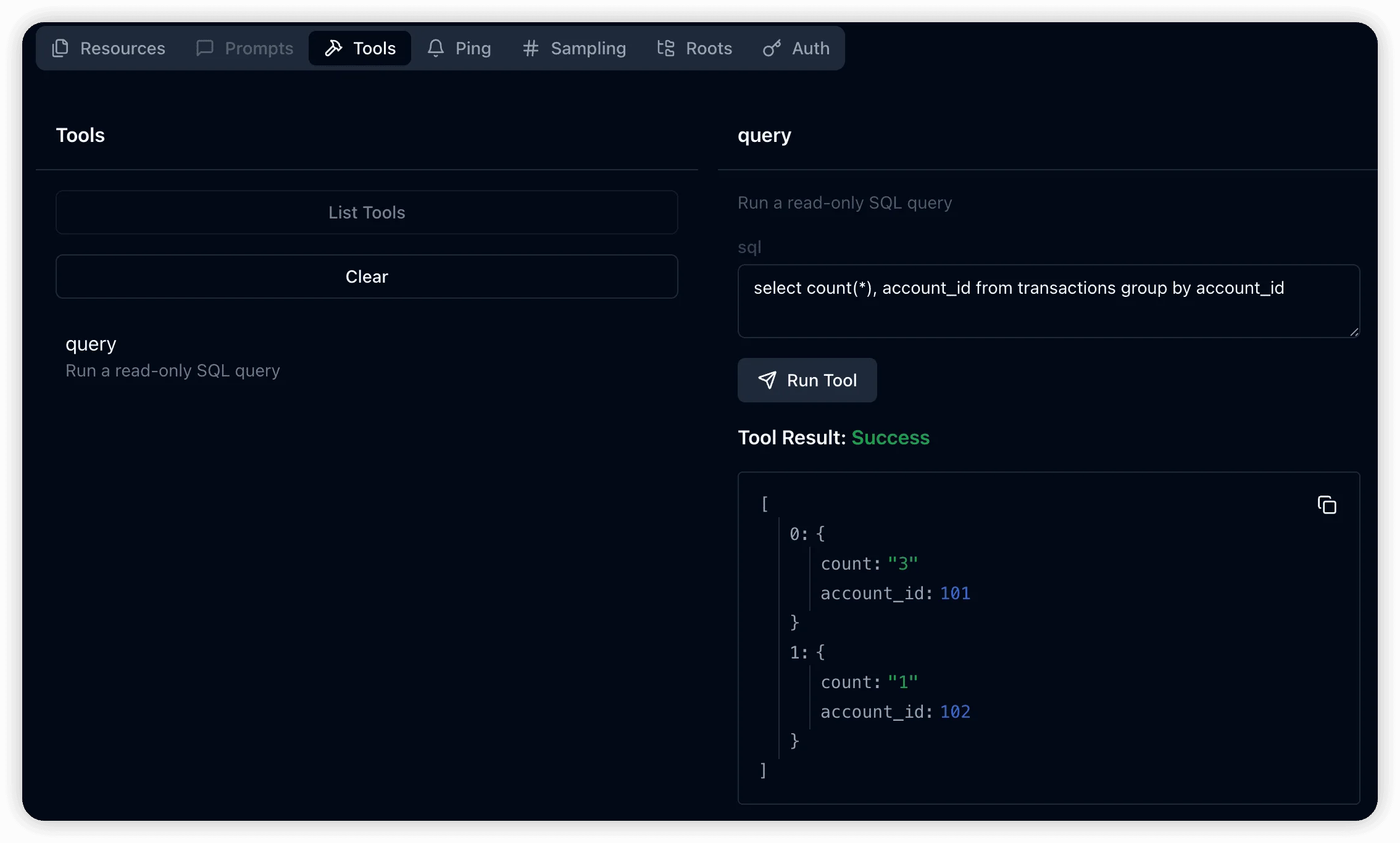
Query Execution:
tools/list: Display available query interface definitionstools/call: Execute specific SQL queries on the database
DBHub MCP Gateway
DBHub is an open-source multi-database MCP gateway that extends beyond the official server-postgres implementation. It supports multiple database systems and provides enhanced resource templates for comprehensive database exploration.
Enhanced Features
- Multiple database support: PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQL Server, and more
- SSE transport protocol: Server-Sent Events for real-time communication
- Extended resource templates: Table schemas, index structures, stored procedures
- Enhanced metadata access: Comprehensive database introspection
Starting DBHub
Launch DBHub with enhanced capabilities:
docker run -p 8080:8080 bytebase/dbhub \
--transport sse \
--dsn "postgres://username:password@host:port/database"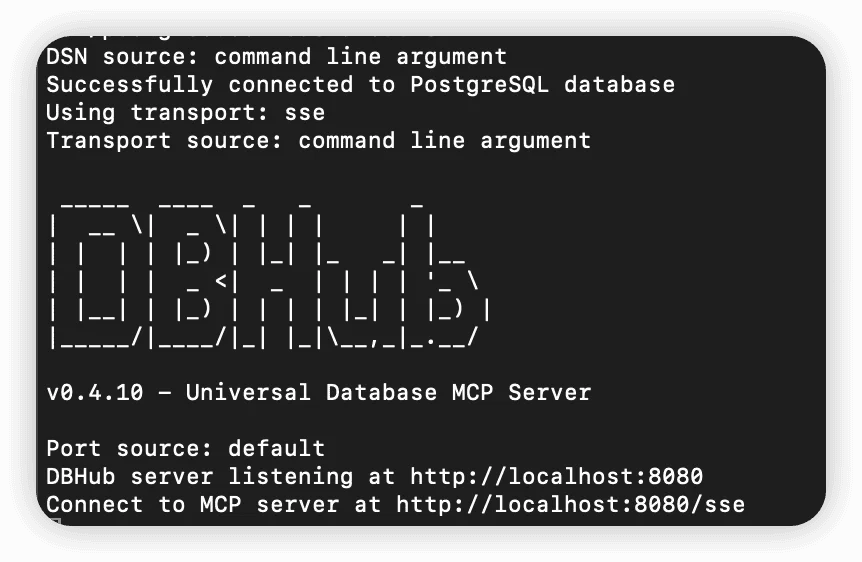
Connecting Inspector to DBHub
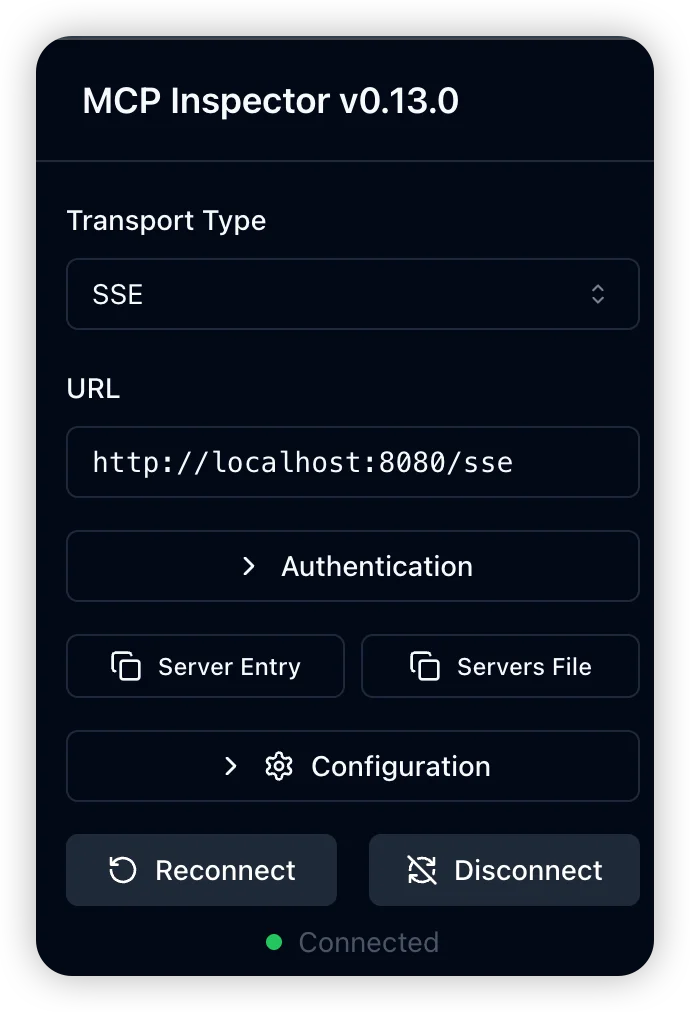
Configure MCP Inspector to connect to the running DBHub service:
Connection Parameters:
- Transport Protocol: SSE (Server-Sent Events)
- URL:
http://localhost:8080/sse
After clicking “Connect,” you should see a “Connected” status indicator.
DBHub Advanced Features
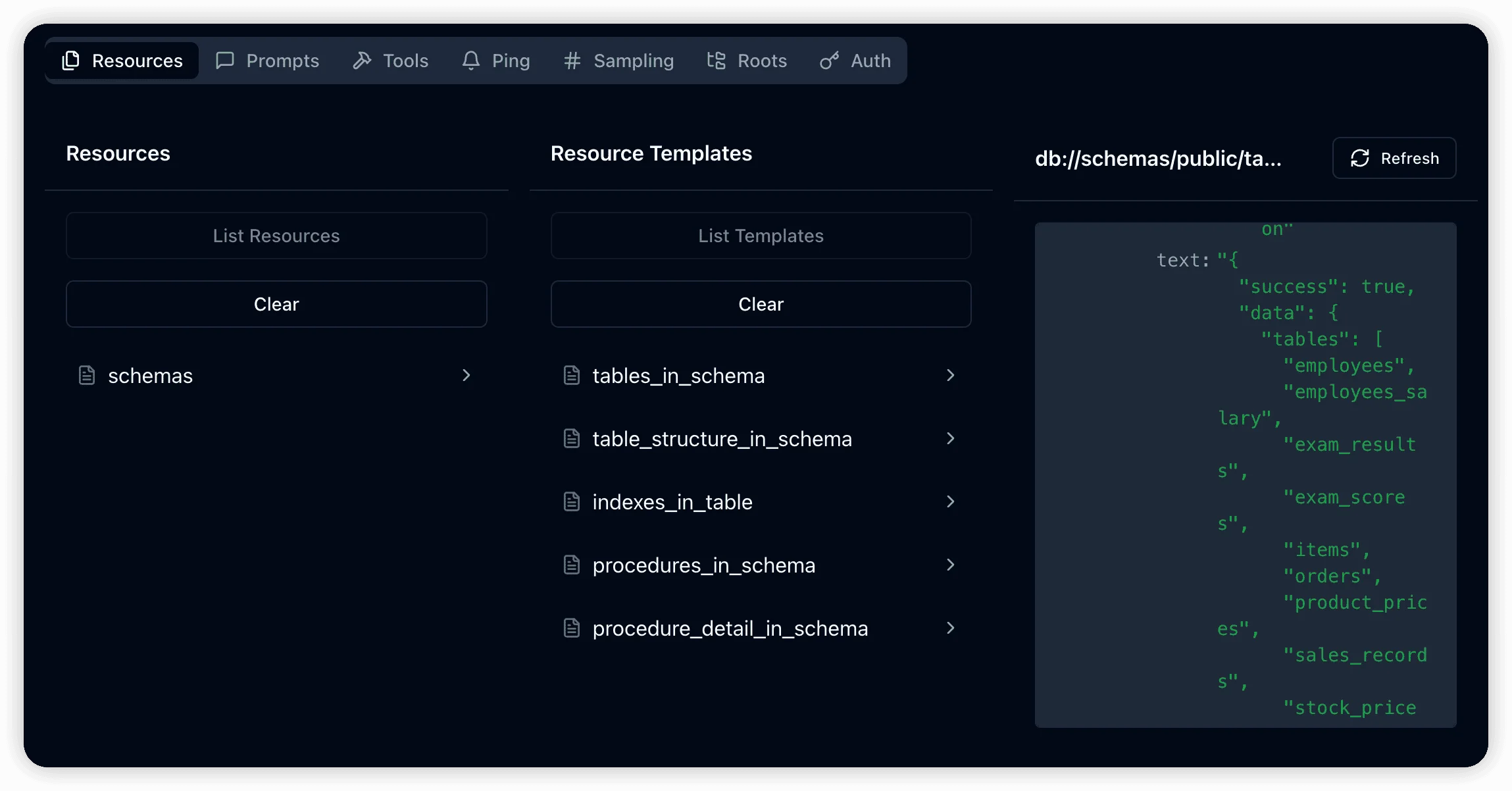
Extended Resource Templates:
DBHub supports the resources/templates/list command, providing access to a broader range of database metadata beyond basic table information.
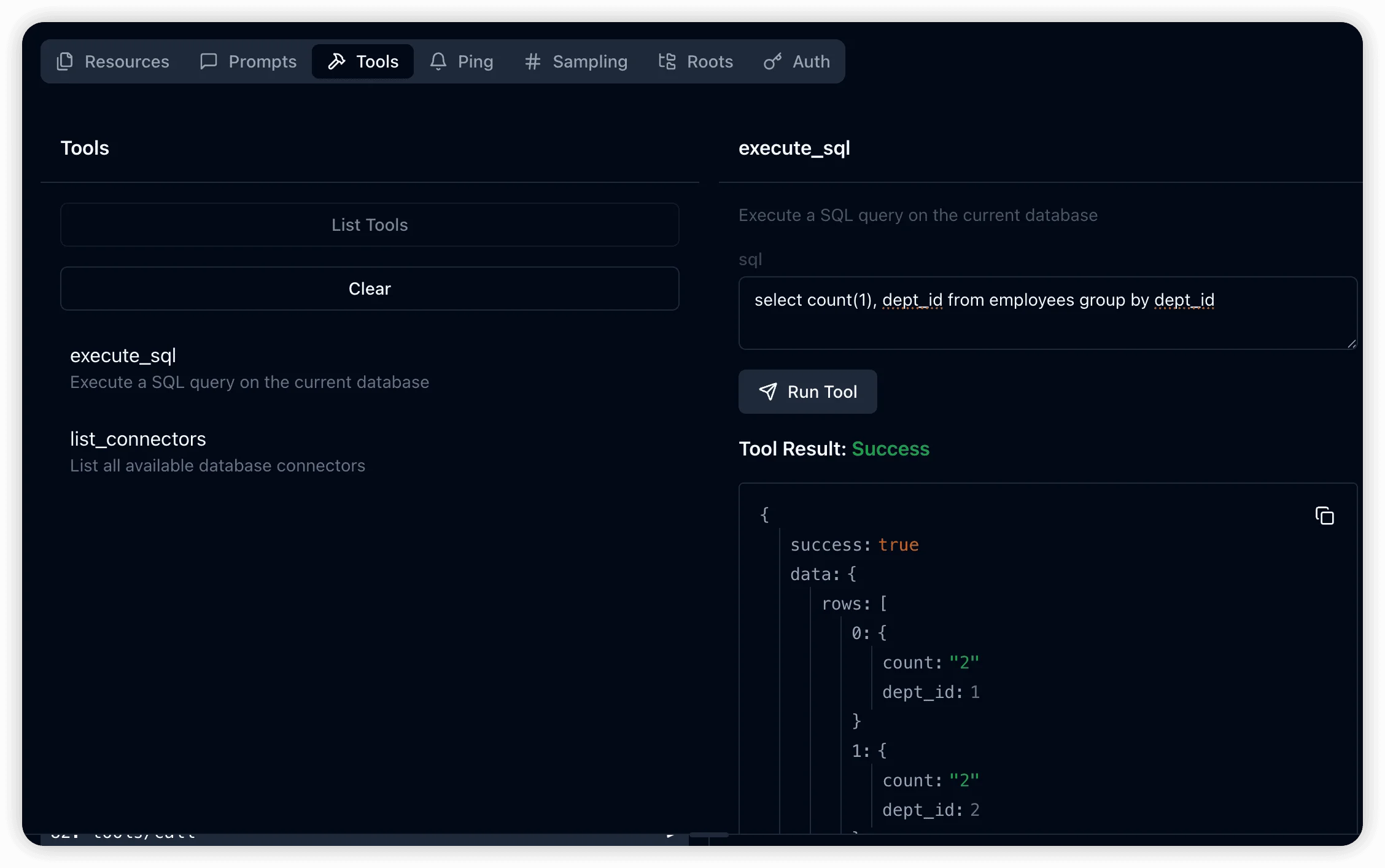
Enhanced Query Interface:
The tools/list command reveals the execute_sql interface, enabling clients to submit custom SQL queries with enhanced error handling and result formatting.
Best Practices
Security Considerations
- Always use read-only database connections for MCP servers
- Implement proper authentication and authorization
- Regularly rotate connection credentials
- Monitor query patterns for unusual activity
Performance Optimization
- Configure appropriate connection pooling
- Set reasonable query timeouts
- Implement query result caching where appropriate
- Monitor resource usage and scale accordingly
Integration Tips
- Test thoroughly with MCP Inspector before production deployment
- Document your schema and available queries for AI agents
- Implement proper error handling and logging
- Consider implementing rate limiting for public endpoints