Features
Explore Tacnode's capabilities — unified storage, real-time indexing, vector search, and more.
Unified Context, Every Workload
Tacnode Context Lake maintains shared, live, and semantic context in a single system. This page covers the technical capabilities that make this possible.

Distributed Relational Database
Tacnode is a distributed relational database with full ACID transactions.

Single-machine relational databases face performance bottlenecks that limit their ability to meet business demands. Tacnode enables horizontal scaling — add machines and resources to increase throughput. Distributed transaction support ensures strong data consistency during expansion.
Key capabilities:
- Horizontal scaling with distributed transactions
- Serializable isolation for strong consistency
- JSON type for semi-structured data
- Vector type for embeddings and AI workloads
Flexible Data Modeling
Tacnode handles structured, semi-structured, and vector data within the same transactional system.

Structured data: Traditional tables with schemas, foreign keys, and referential integrity.
Semi-structured data: The JSON type handles schema-flexible documents. Unlike document databases that struggle with many-to-many relationships, Tacnode combines JSON flexibility with relational joins and foreign keys — giving you the best of both models.
Vector data: Native support for embeddings enables semantic search, recommendations, and RAG. Vectors are stored alongside structured data, not in a separate system.
SQL support means complex queries — joins, aggregations, window functions — work across all data types.
Unified Search
Tacnode provides integrated search capabilities without a separate search engine.

Full-text search: Inverted indexes, relevance ranking, and text analysis.
Vector search: Similarity search over embeddings with HNSW indexes.
Omni Search: Combine keyword, structured filters, and vector similarity in a single query.
Because search is integrated into the Context Lake, results are always based on current data. No synchronization lag between your database and search engine. No data inconsistency.
Real-Time Analytics
Tacnode functions as a real-time analytics engine with millisecond query latency.

Traditional data warehouses ingest data in batches, achieving good performance but lacking real-time capabilities. Data latency is measured in hours or minutes.
Some systems support real-time ingestion but only guarantee eventual consistency — meaning queries might see incomplete transactions or stale state.
Tacnode delivers:
- Real-time ingestion: Data becomes queryable the instant it arrives
- Strong consistency: Full ACID transactions, not eventual consistency
- Low latency: Millisecond-level interactive queries
- High concurrency: Multiple workloads operate in parallel
Incremental Materialized Views
Define transformations in SQL. They execute continuously as data arrives.
- No external orchestration or batch scheduling
- Features, aggregations, and derived context stay consistent with live state
- Changes propagate incrementally — no full recomputation
Workload Isolation
Multiple workloads operate against shared context without interfering with each other.

- Nodegroups: Independent compute resources that scale separately
- Resource isolation: Analytical queries don’t block transactions
- Performance guarantees: Ingestion doesn’t slow retrievals
Developer Experience
Tacnode is PostgreSQL-compatible, making it accessible to teams that don’t want to learn a new stack.
- PostgreSQL wire protocol: Use existing drivers, ORMs, and tools
- Standard SQL: Your SQL knowledge transfers directly
- Familiar tooling: Connect with psql, DBeaver, DataGrip, or any PostgreSQL client
Data Synchronization
Built-in data sync from external sources into the Context Lake.
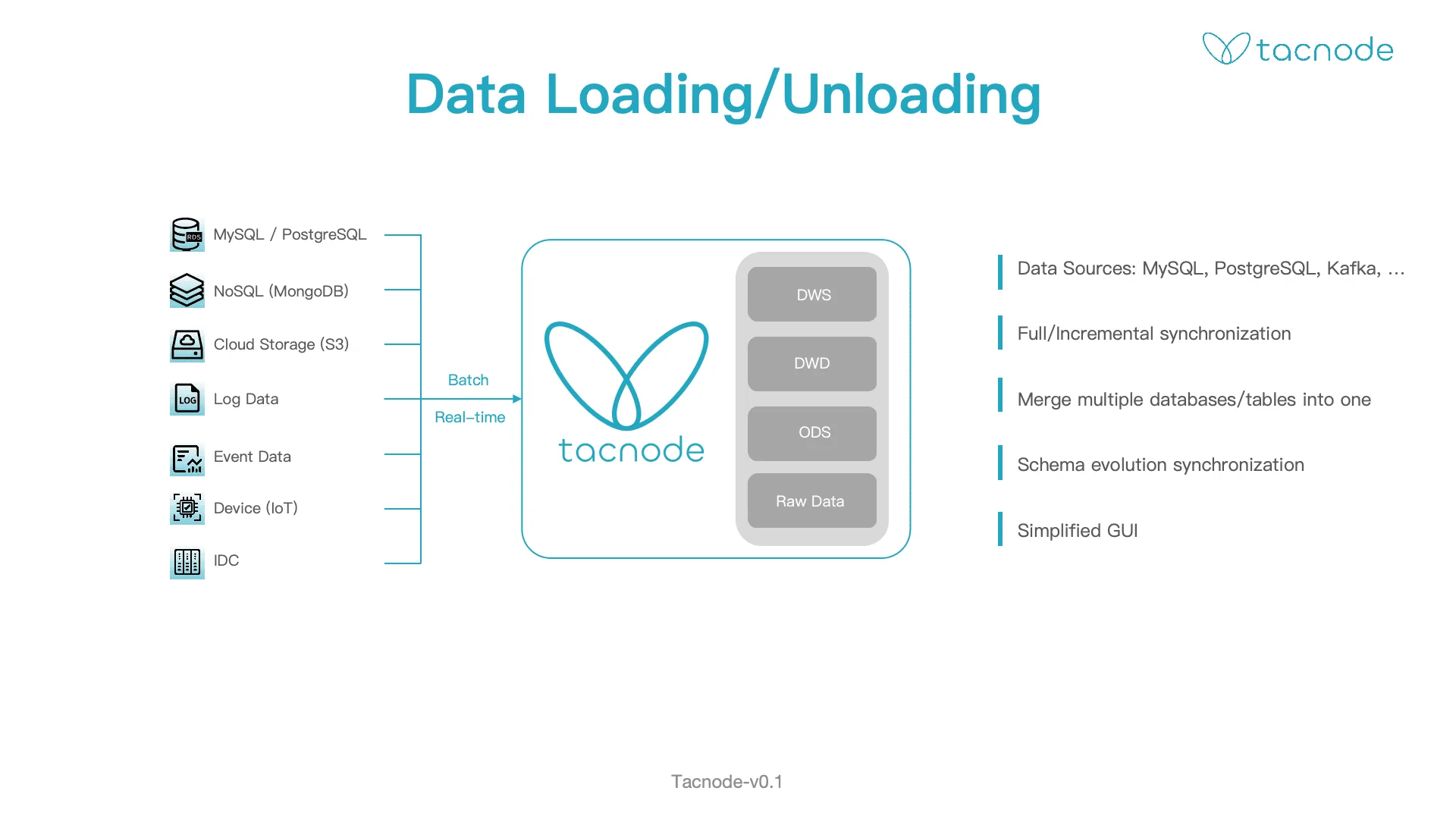
- Source support: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, Kafka, and more
- Sync modes: Full synchronization, incremental CDC, or both
- Sharded sources: Consolidate sharded tables into a single table automatically
- Schema evolution: Handles upstream schema changes — new tables, new columns, type changes